Plantar Fasciitis vs. Stress Fractures
If you're experiencing foot pain, it can be difficult to determine the cause. Plantar fasciitis and stress fractures are two common foot injuries that can cause similar symptoms but have different causes and treatments. This article will explore the differences between plantar fasciitis and stress fractures and how to diagnose and treat these conditions properly.
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot injury that causes pain in the heel and arch of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running across the foot's bottom, becomes inflamed. This inflammation can be caused by several factors, including overuse, obesity, and having high arches or flat feet.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The most common symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain that is worse in the morning or after rest periods. The pain may also be worse when standing for long periods or after physical activity. In some cases, the pain may radiate into the arch of the foot or toes.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
As mentioned above, plantar fasciitis is often caused by overuse. This can occur in physically active people, such as runners or dancers, or those who stand for long periods on hard surfaces. Other factors contributing to plantar fasciitis include obesity, high arches or flat feet, and wearing shoes that do not provide proper support.

What are Stress Fractures?
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone that occurs due to repetitive stress or overuse. These fractures are most common in the feet and lower legs and are often seen in athletes who engage in high-impact sports such as running or basketball.
Symptoms of Stress Fractures
The main symptom of a stress fracture is a pain in the affected bone. The pain may be constant or only occur during certain activities, such as running or jumping. The pain may also worsen at night or when applying pressure to the affected area.
Causes of Stress Fractures
As mentioned above, stress fractures are typically caused by repetitive stress or overuse. This can occur in people who engage in high-impact sports or activities or those with sudden increases in their physical activity levels. Other factors that may contribute to the development of stress fractures include having weak bones due to osteoporosis or other conditions and wearing shoes that do not provide proper support.
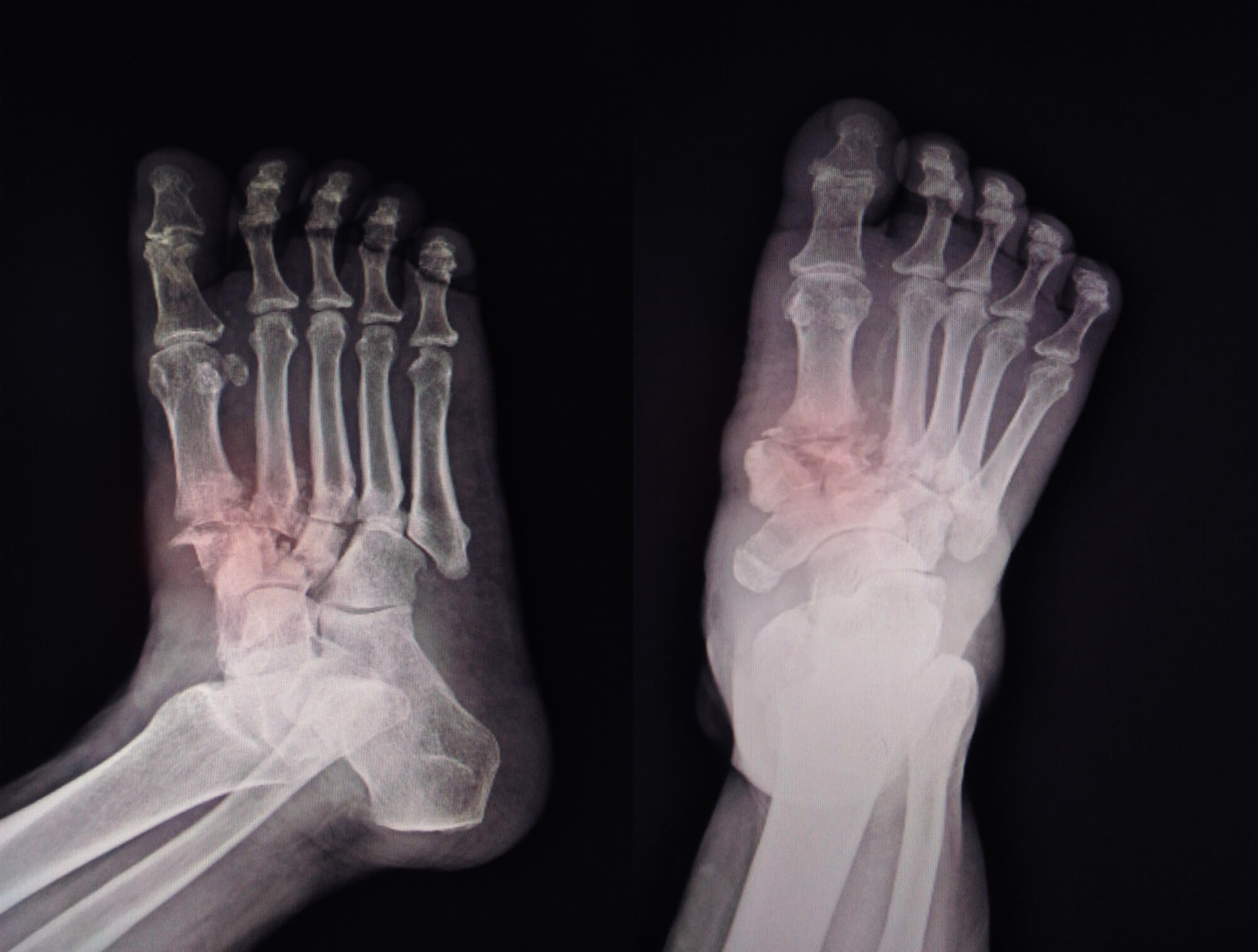
How are Plantar Fasciitis and Stress Fractures Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis
If you suspect you have plantar fasciitis, you must see a podiatrist or other medical professional for a proper diagnosis. A podiatrist may ask about your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical examination of your foot. In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs may be necessary to rule out other potential causes of foot pain.
Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis
Treatment for plantar fasciitis may include rest, ice, and stretching exercises to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Your podiatrist may also recommend physical therapy or the use of orthotic inserts to help correct any underlying foot problems that may be contributing to your plantar fasciitis. In severe cases, a corticosteroid injection may be necessary to reduce inflammation.
Diagnosis of Stress Fractures
Like plantar fasciitis, a medical professional, such as a podiatrist, should diagnose stress fractures. Your podiatrist will ask about your symptoms and medical history and may also perform a physical examination of your foot. Imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs may also be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of a stress fracture.
Treatment of Stress Fractures
Treatment for stress fractures typically involves rest and crutches to keep weight off the affected bone. Your podiatrist may also recommend physical therapy to help strengthen the muscles surrounding the fractured bone. A cast or boot may be necessary to keep the bone immobilized while it heals.
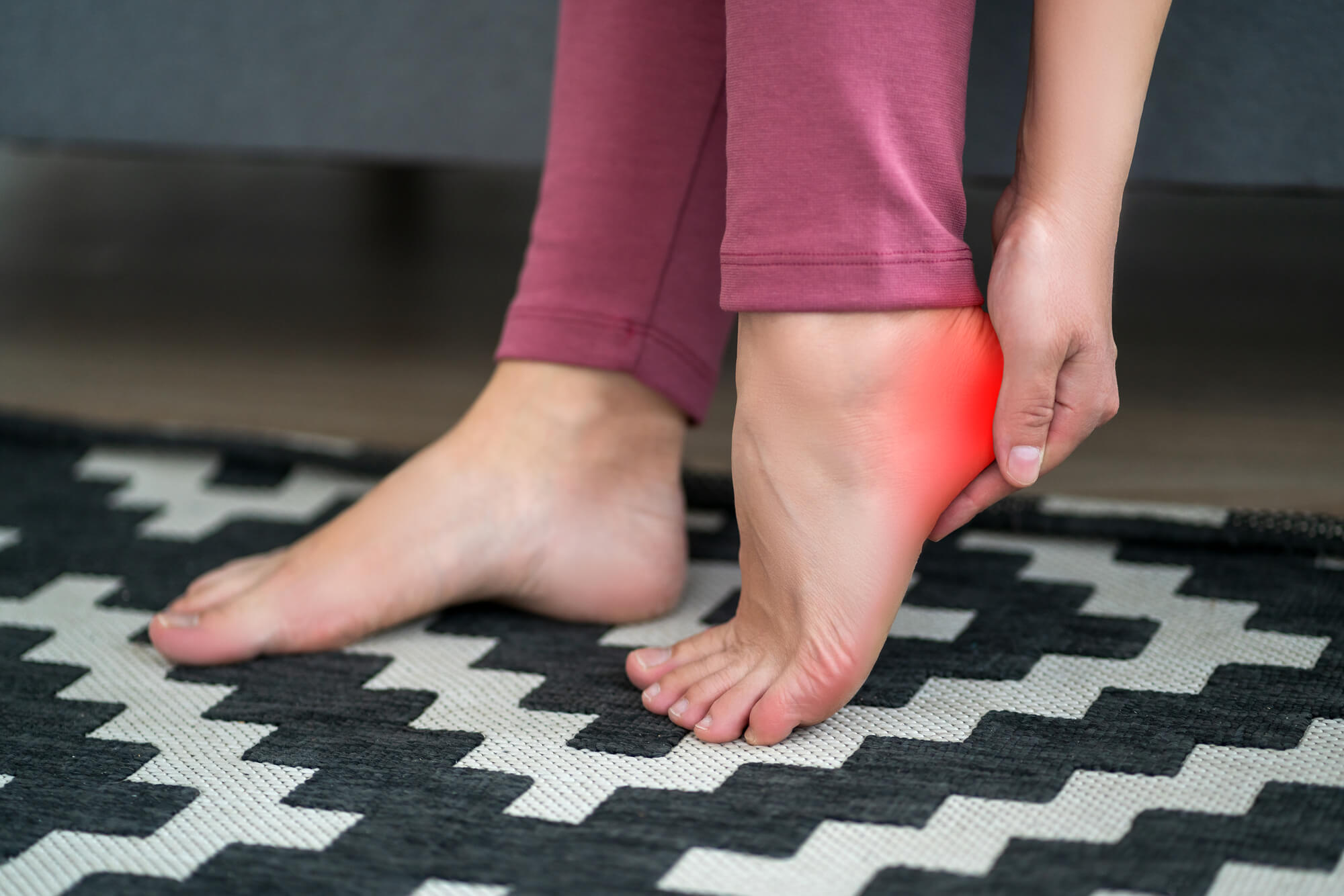
Preventing Plantar Fasciitis and Stress Fractures
Tips for Preventing Plantar Fasciitis
To prevent plantar fasciitis, it's important to wear shoes that provide proper support and cushioning, especially if you're physically active or stand for long periods. Stretching your feet and calves regularly can also help prevent plantar fasciitis. If you're starting a new exercise program, it's important to gradually increase your activity levels to give your feet and legs time to adjust.
Tips for Preventing Stress Fractures
To prevent stress fractures, it's important to wear shoes that provide proper support and cushioning, especially if you're physically active. Gradually increasing your activity levels and taking breaks to rest your feet can also help prevent stress fractures. It's also important to pay attention to your body and listen to any pain or discomfort you may be experiencing. If you're experiencing pain, it's important to take a break and rest until it subsides.
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis and stress fractures are two common foot injuries that can cause similar symptoms. However, these conditions have different causes and treatments. If you're experiencing foot pain, it's important to see a medical professional, such as a podiatrist, for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Following proper prevention techniques and listening to your body can help reduce your risk of developing plantar fasciitis or stress fractures.
FAQ
What is plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot injury that causes pain in the heel and arch of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue running across the foot's bottom, becomes inflamed.
What are the symptoms of plantar fasciitis?
The most common symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain that is worse in the morning or after rest periods. The pain may also be worse when standing for long periods or after physical activity. In some cases, the pain may radiate into the arch of the foot or toes.
What are the causes of plantar fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is often caused by overuse. This can occur in physically active people, such as runners or dancers, or those who stand for long periods on hard surfaces. Other factors contributing to plantar fasciitis include obesity, high arches or flat feet, and wearing shoes that do not provide proper support.
What is a stress fracture?
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone that occurs due to repetitive stress or overuse. These fractures are most common in the feet and lower legs and are often seen in athletes who engage in high-impact sports such as running or basketball.
What are the symptoms of a stress fracture?
The main symptom of a stress fracture is a pain in the affected bone. The pain may be constant or only occur during certain activities, such as running or jumping. The pain may also worsen at night or when applying pressure to the affected area.
What are the causes of stress fractures?
Stress fractures are typically caused by repetitive stress or overuse. This can occur in people who engage in high-impact sports or activities or sudden increases in their physical activity levels. Other factors that may contribute to the development of stress fractures include having weak bones due to osteoporosis or other conditions and wearing shoes that do not provide proper support.
How is a stress fracture different from a heel stress fracture?
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone due to repetitive stress or overuse, while a heel stress fracture specifically refers to a stress fracture in the calcaneus (heel bone).
What is the calcaneus?
The calcaneus, also known as the heel bone, is the largest bone in the foot and is located at the back of the foot.

