Identifying and Treating Common Foot Infections
Keeping the feet healthy is crucial to our overall well-being, but the feet are often overlooked. If left untreated, foot problems can cause discomfort and pain, leading to more severe conditions. One of the most common foot problems is a foot infection. Foot infections can range from mild to severe and affect any part of the foot, including the toenails, soles, and skin. This article will explore common foot infections and their symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options.
Types of Foot Infections
Various types of foot infections can affect any part of the foot. Identifying the type of infection is important to determine the most effective treatment. Here are the most common types of foot infections and their symptoms:
Fungal Infections
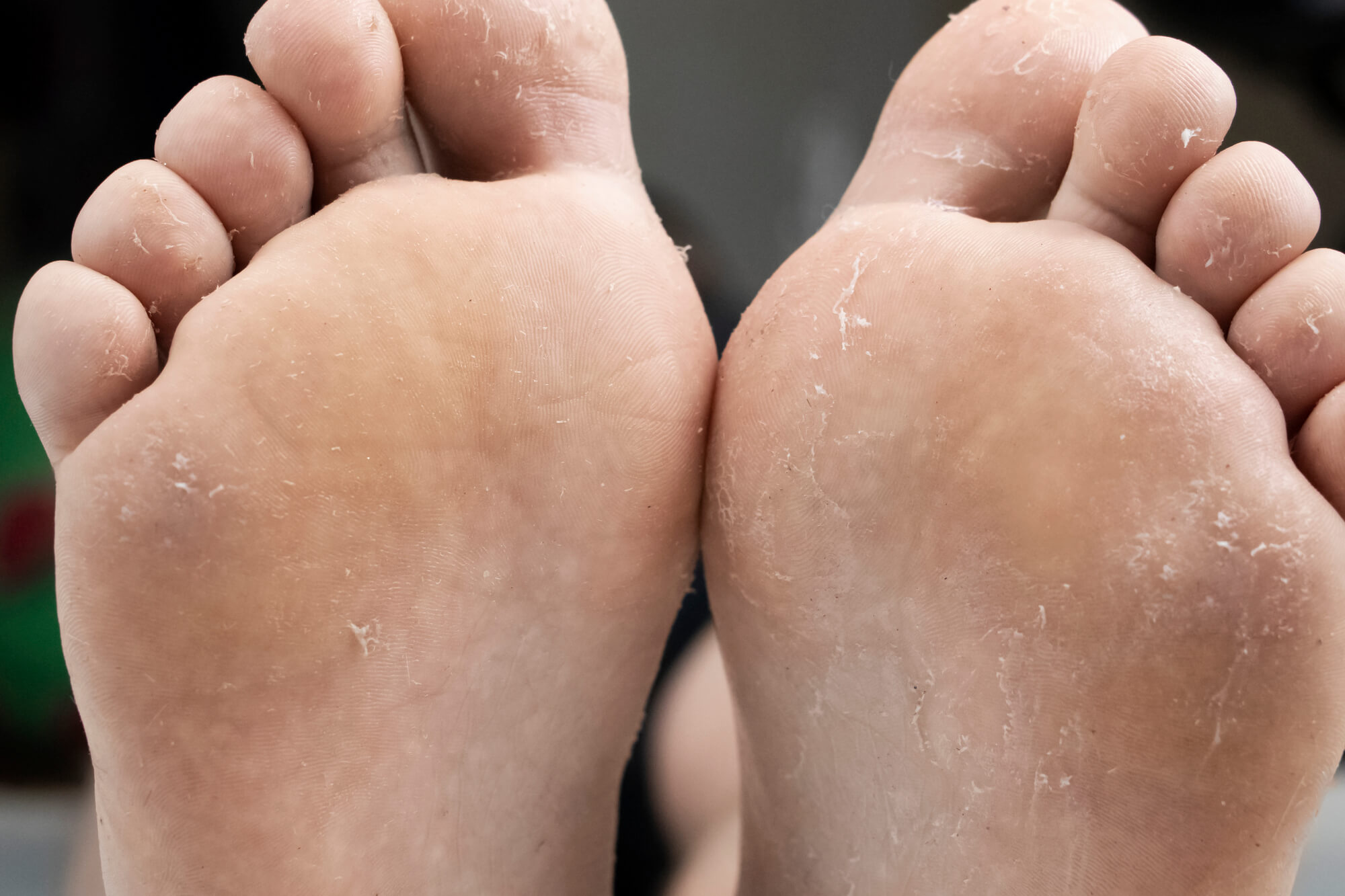
Fungal infections are one of the most common foot problems. They can affect any part of the foot, including the skin, toenails, and soles. The most common type of fungal infection is athlete's foot, which usually affects the skin between the toes. Symptoms of fungal infections include:
- Dry, itchy, and scaly skin
- Redness and swelling
- Cracking and peeling skin
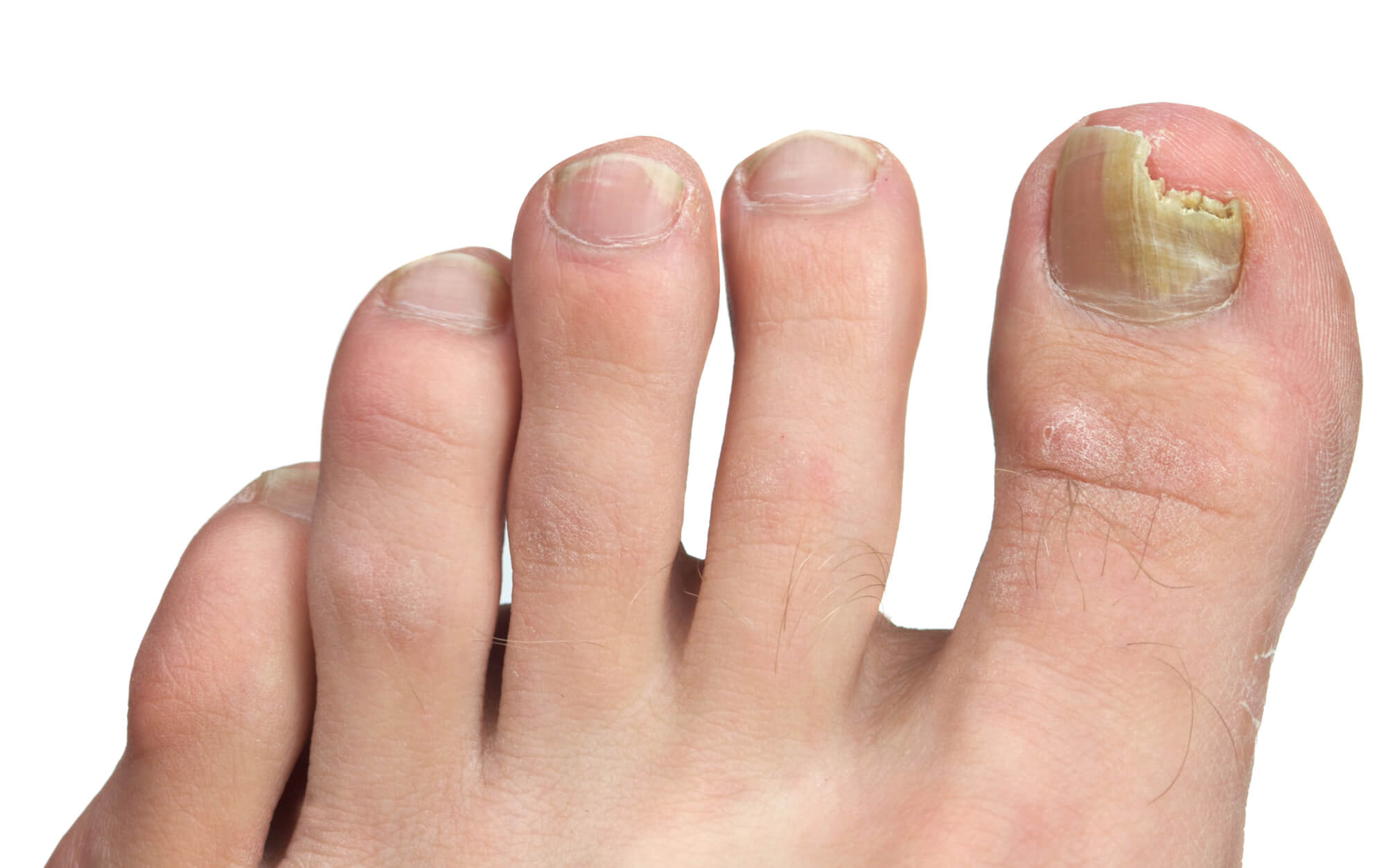
- Discolored, thickened, or brittle toenails
Fungal infections are contagious and can be easily spread from person to person or from one part of the body to another. They thrive in warm and moist environments, making getting them easily in places like swimming pools, showers, or gyms.
Treating fungal infections requires antifungal medication, which can be in the form of a cream or pill. Topical antifungal medication is generally effective for mild cases, while more severe cases may require oral antifungal medication.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are less common than fungal infections but can still cause severe foot problems. They usually occur due to a break in the skin, such as a cut, scrape, or insect bite. Symptoms of bacterial infections include:
- Redness, warmth, and swelling
- Pain and tenderness
- Pus or drainage
- Fever
If left untreated, bacterial infections can spread to other parts of the foot or even the bloodstream, which can be life-threatening. The treatment of bacterial infections usually requires antibiotic medication. Topical antibiotic creams are generally effective for mild cases, while more severe cases may require oral antibiotics.
Viral Infections
Viral infections are less common than fungal and bacterial infections but can still cause significant foot problems. Some common viral foot infections include plantar warts, caused by the human papillomavirus, and herpes, which can cause foot blisters. Symptoms of viral infections include:
- Blisters or lesions on the foot
- Redness and swelling
- Pain or discomfort when walking or standing
- Itching or burning sensations on the foot
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and body aches
- Discoloration or darkening of the affected area
- Tingling or numbness in the foot
- Formation of scabs or crusts over the affected area
Treatment options for viral infections vary depending on the type of virus. Plantar warts can be treated with salicylic acid or cryotherapy, while herpes requires antiviral medication.

Common Foot Infections
Foot infections are a common health concern as our feet are constantly exposed to various bacteria and fungi, making them susceptible to infections. Identifying the type of infection is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment. Here are some common foot infections:
Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection that usually affects the skin between the toes but can also affect the soles of the feet. It is highly contagious and transmitted through direct or indirect contact with an infected person or surface. It thrives in warm and moist environments, making it easy to contract the infection in public places such as locker rooms or pools. Symptoms of athlete's foot include itching, burning, and redness in the affected area. In severe cases, blisters may form, and the skin may crack and peel. To prevent athlete's foot, it is essential to keep your feet clean and dry, wear clean socks, and avoid walking barefoot in public places.
Toenail Fungus
Toenail fungus is a fungal infection that affects the toenails, causing them to become thick, discolored, and brittle. It can also cause the separation of the nail from the nail bed, making it painful to walk or wear shoes. Toenail fungus is highly contagious and can be contracted through direct or indirect contact with an infected person or surface. It thrives in warm and moist environments, making contracting the infection easy in public places. To prevent toenail fungus, it is essential to keep your feet clean and dry, wear clean socks, and avoid sharing nail clippers or other tools with an infected person.
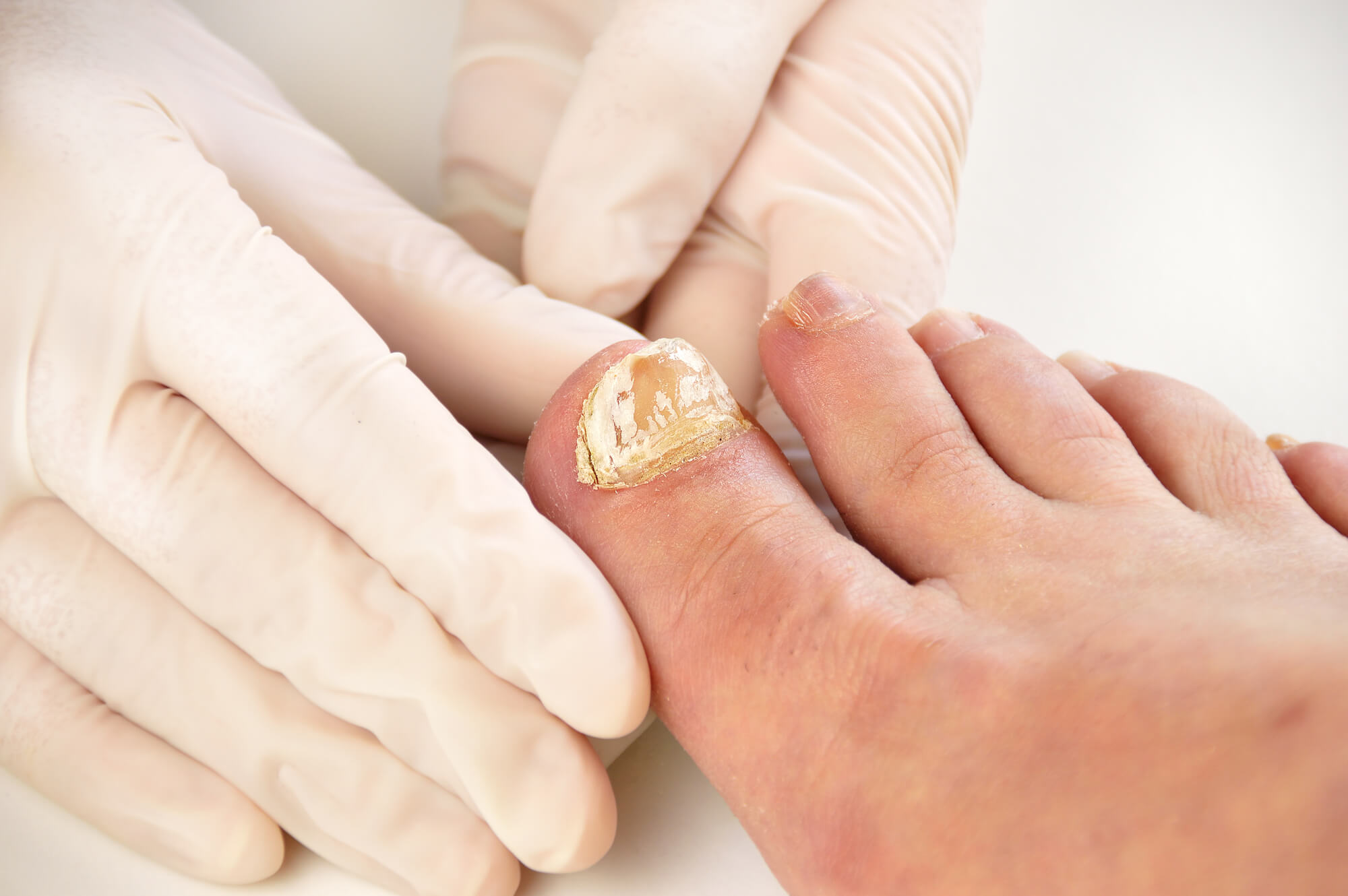
Ingrown Toenail
Ingrown toenails occur when the corner or side of the toenail grows into the skin, leading to pain, swelling, and infection. It is usually caused by improper nail trimming, wearing ill-fitting shoes, or having naturally curved nails. Ingrown toenails are common in the big toe and can be painful if left untreated. To prevent ingrown toenails, it is important to trim your nails straight across, avoid wearing tight shoes, and wear shoes with a wide toe box.
Blisters
Blisters are fluid-filled sacs that can form on the skin of the feet due to friction or pressure. They are often painful and can become infected if not treated properly. Blisters are usually caused by ill-fitting shoes or walking or running for long periods without adequate cushioning. To prevent blisters, it is important to wear shoes that fit properly, provide adequate support, and gradually increase the duration and intensity of physical activity to avoid overuse injuries.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that can occur on the skin of the feet, causing redness, swelling, and warmth. It can be serious if not treated promptly and can spread quickly to other parts of the body. A break in the skin, such as a cut, scrape, or insect bite, usually causes cellulitis. It can also occur as a complication of an ingrown toenail or an untreated blister. To prevent cellulitis, it is important to keep your feet clean and dry, avoid walking barefoot in public places and treat any cuts or wounds promptly.
Risk Factors for Foot Infections
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing foot infections. Some of the most common risk factors include:
- Diabetes and other chronic illnesses can affect blood flow and immune system function
- Weakened immune system due to medication, radiation therapy, or other factors
- Poor hygiene, especially in the feet
- Exposure to contaminated surfaces, such as public showers or swimming pools
- Ill-fitting shoes, especially high heels or shoes that do not provide adequate support
When to See a Podiatrist
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect a foot infection. Signs that an infection may be serious include:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Redness that spreads to other parts of the foot
- Fever
- Pus or discharge
- Numbness or tingling
Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent the infection from becoming more severe and spreading to other parts of the foot or body. Podiatrists are trained to diagnose and treat foot infections and can provide effective treatment options.
Treatment Options for Foot Infections
The treatment of foot infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Sometimes, simple topical cream or ointment may be enough to clear up the infection. More aggressive treatment options, such as surgery or oral medications, may be necessary in other cases.
Topical Medications
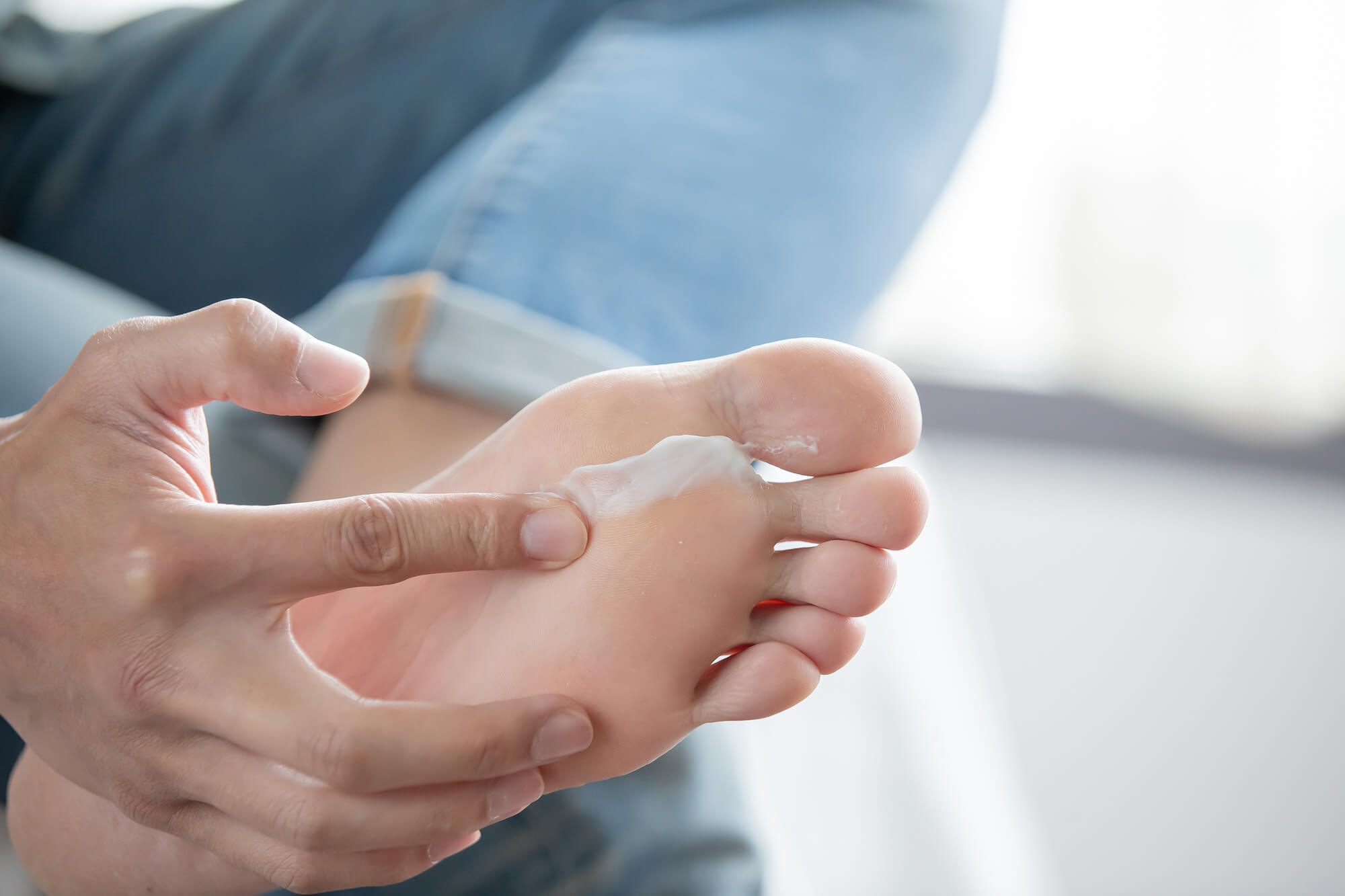
For mild cases of foot infections, topical medications, such as antifungal creams or antibiotic ointments, may effectively treat the infection. Antifungal creams, such as clotrimazole or terbinafine, are commonly used to treat fungal infections. These creams work by stopping the growth of the fungus and preventing it from spreading.
Antibiotic ointments like mupirocin or neomycin are commonly used to treat bacterial infections. These ointments work by killing the bacteria that are causing the infection and preventing it from spreading.
Oral Medications
For more severe cases of foot infections, oral medications, such as antifungal pills or antibiotics, may be necessary. Antifungal pills, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, are commonly used to treat severe cases of fungal infections. These pills work by killing the fungus that is causing the infection.
Antibiotics, such as amoxicillin or cephalexin, are commonly used to treat severe cases of bacterial infections. These antibiotics kill the bacteria causing the infection and prevent it from spreading.

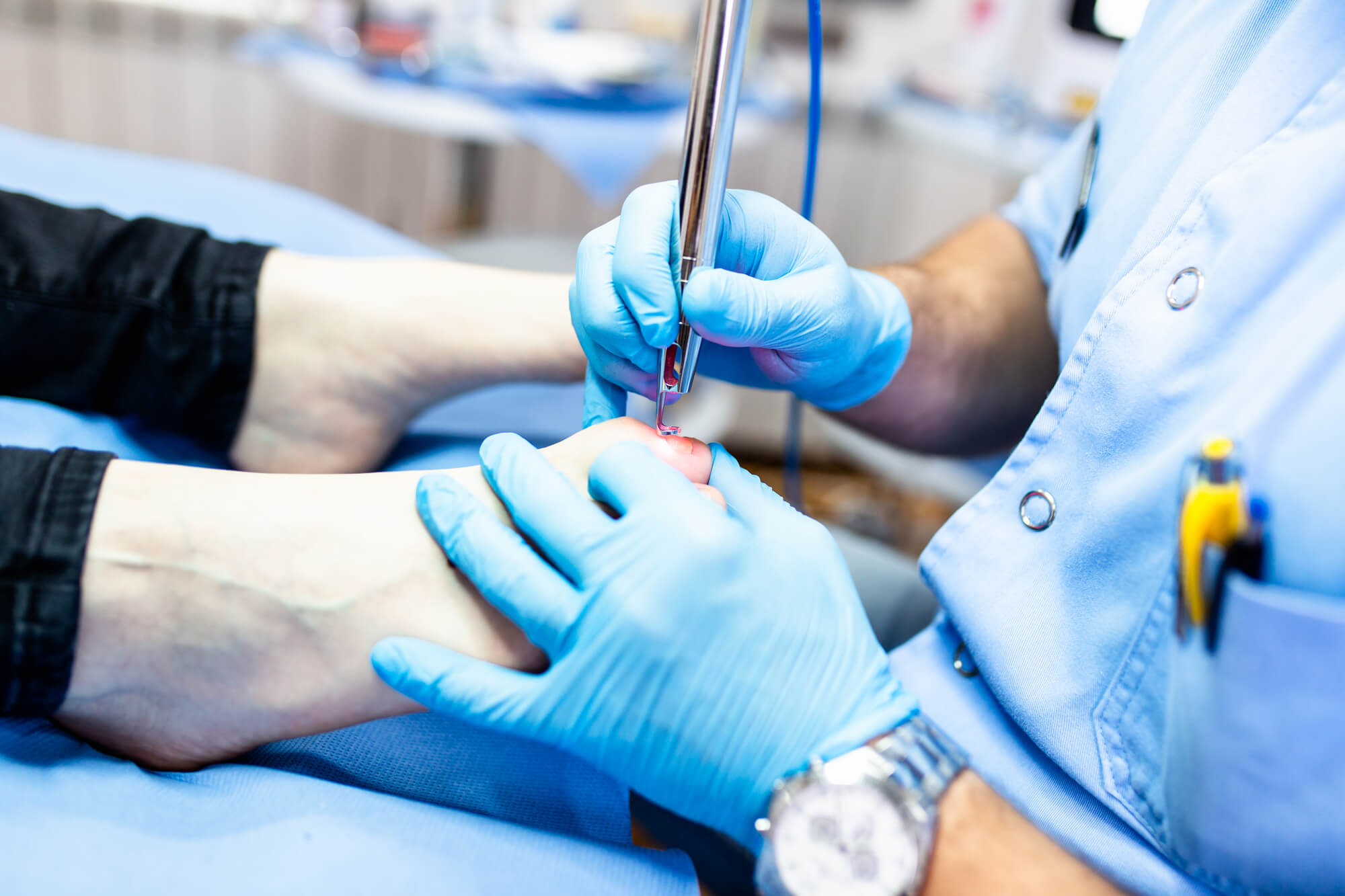
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat foot infections. For example, in severe cases of an ingrown toenail, the podiatrist may need to remove a portion of the toenail to relieve the pressure and prevent the infection from spreading. In severe cases of plantar fasciitis, the podiatrist may need to perform surgery to remove damaged tissue or release the tension in the ligament.
Prevention Tips
Prevention is key when it comes to foot infections. Here are some tips to help prevent foot infections:
- Keep your feet clean and dry.
- Wear clean socks and change them daily.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public places, such as locker rooms or showers.
- Wear shoes that fit properly and provide adequate support.
- Avoid wearing high heels for extended periods.
- Promptly treat foot problems, such as corns, calluses, or bunions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foot infections are common foot problems that can cause discomfort and pain and lead to more severe conditions if left untreated. Fungal, bacterial, and viral infections can affect any part of the foot, including the toenails, soles, and skin. It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect a foot infection. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent the infection from becoming more severe and spreading to other parts of the foot or body.
Podiatrists are trained to diagnose and treat foot infections and can provide effective treatment options. Prevention is key regarding foot infections, and following the prevention tips mentioned above can help keep your feet healthy and free from infections. Remember to take care of your feet and seek medical attention if you notice any signs of a foot infection.

