The Connection Between Diabetes and Foot Fungus
If you have diabetes, you're more likely to develop foot fungus. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Foot fungus is a common problem that affects many people, but for people with diabetes, it can be especially dangerous.
In this article, we'll explore the link between diabetes and foot fungus, and what you can do to protect yourself from this common condition.
What is Foot Fungus?
Foot fungus is a common condition that occurs when a fungus grows on the skin of the foot. There are several types of foot fungus, including onychomycosis, or nail infection, and tinea pedis, also known as athlete's foot.
Foot fungus is caused by a fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments such as shoes and socks. People with diabetes are more susceptible because high blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage and poor circulation, which can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections.
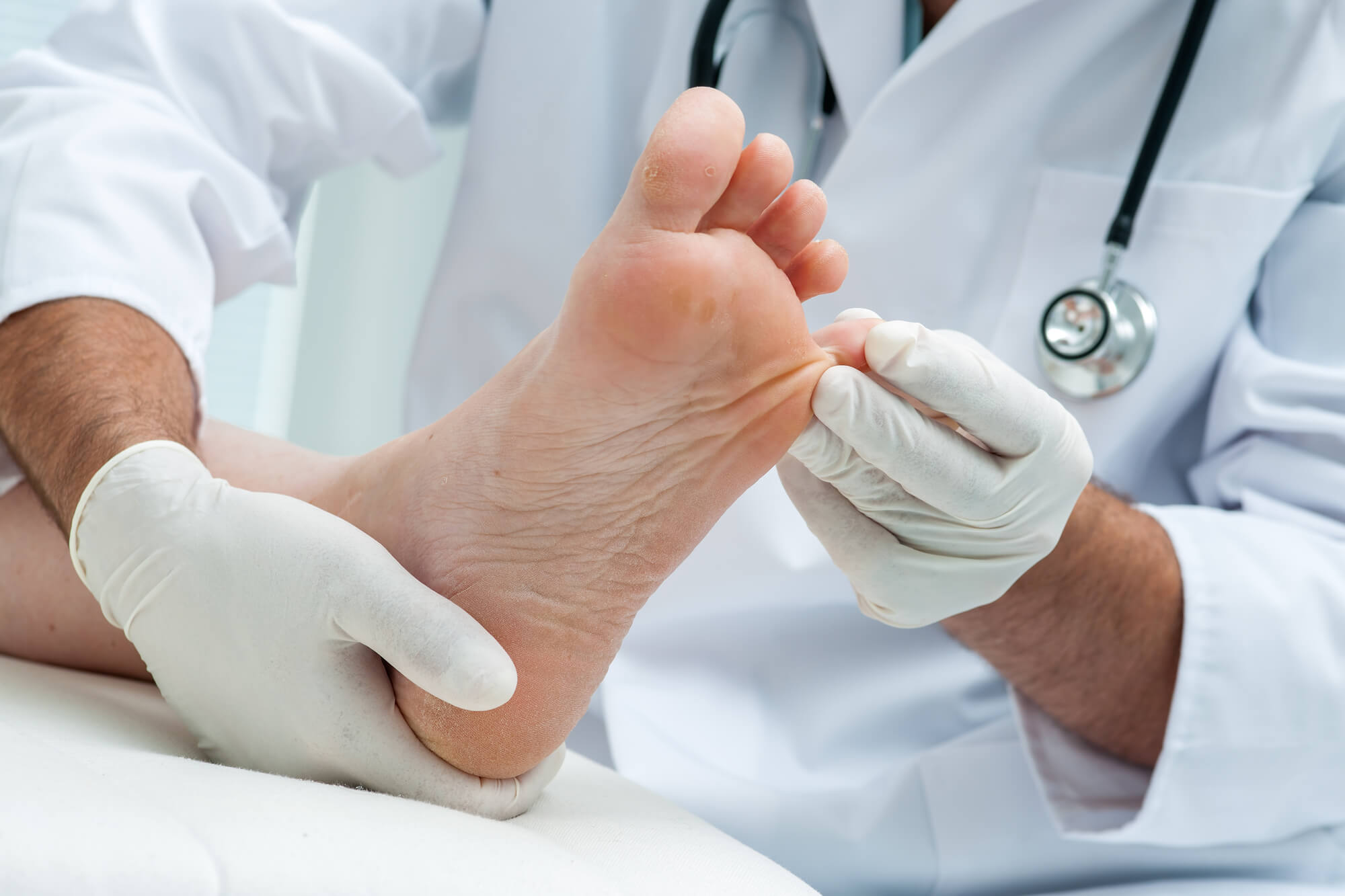
The Connection Between Diabetes and Foot Fungus
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot fungus due to several factors, including poor circulation, nerve damage, and weakened immune systems. In addition, people with type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop onychomycosis, a fungal infection of the toenail.
Types of Foot Fungus
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
Tinea pedis is a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, especially the areas between the toes. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm, moist environments such as sweaty socks and shoes. Symptoms of tinea pedis include redness, itching, and burning of the affected areas, as well as scaling, cracking, and peeling of the skin. In severe cases, blisters may also develop. Treatment for tinea pedis may include over-the-counter antifungal creams or sprays, as well as prescription-strength medications. It's also important to keep the feet dry and clean, and to avoid walking barefoot in public areas.
Onychomycosis (Nail Fungus)
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection that affects the nails of the feet and hands. It is caused by a variety of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. The infection usually begins as a white or yellow spot under the nail, and can spread to the entire nail if left untreated. Symptoms of onychomycosis include thickening and discoloration of the nail, as well as separation of the nail from the nail bed. Treatment for onychomycosis may include topical or oral antifungal medications, laser treatment and nail removal in severe cases.
Other Fungal Infections
In addition to tinea pedis and onychomycosis, several other fungal infections can affect the feet. These include:
- Interdigital Candidiasis: A fungal infection caused by yeast that affects the skin between the toes. Symptoms include itching, burning, and redness of the affected area. Treatment may include antifungal creams or powders.
- Erythrasma: A bacterial infection that can be mistaken for a fungal infection. It is caused by the bacteria Corynebacterium minutissimum and can cause itching, burning, and redness in the affected area. Treatment may include topical antibiotics.
- Pitted Keratolysis: A bacterial infection that causes small pits or craters in the soles of the feet. It is caused by the bacteria Dermatophilus congolensis and can cause a foul odor. Treatment may include topical or oral antibiotics.
- Sporotrichosis: A rare fungal infection that can be transmitted from plants or animals to humans. It can cause a red, painless bump on the skin, which can develop into a larger, ulcerated lesion. Treatment may include antifungal medication or surgery in severe cases.
In general, it's important to seek treatment for foot fungus to prevent the infection from spreading and causing more serious complications. A podiatrist can diagnose the type and recommend the best treatment options for your condition.
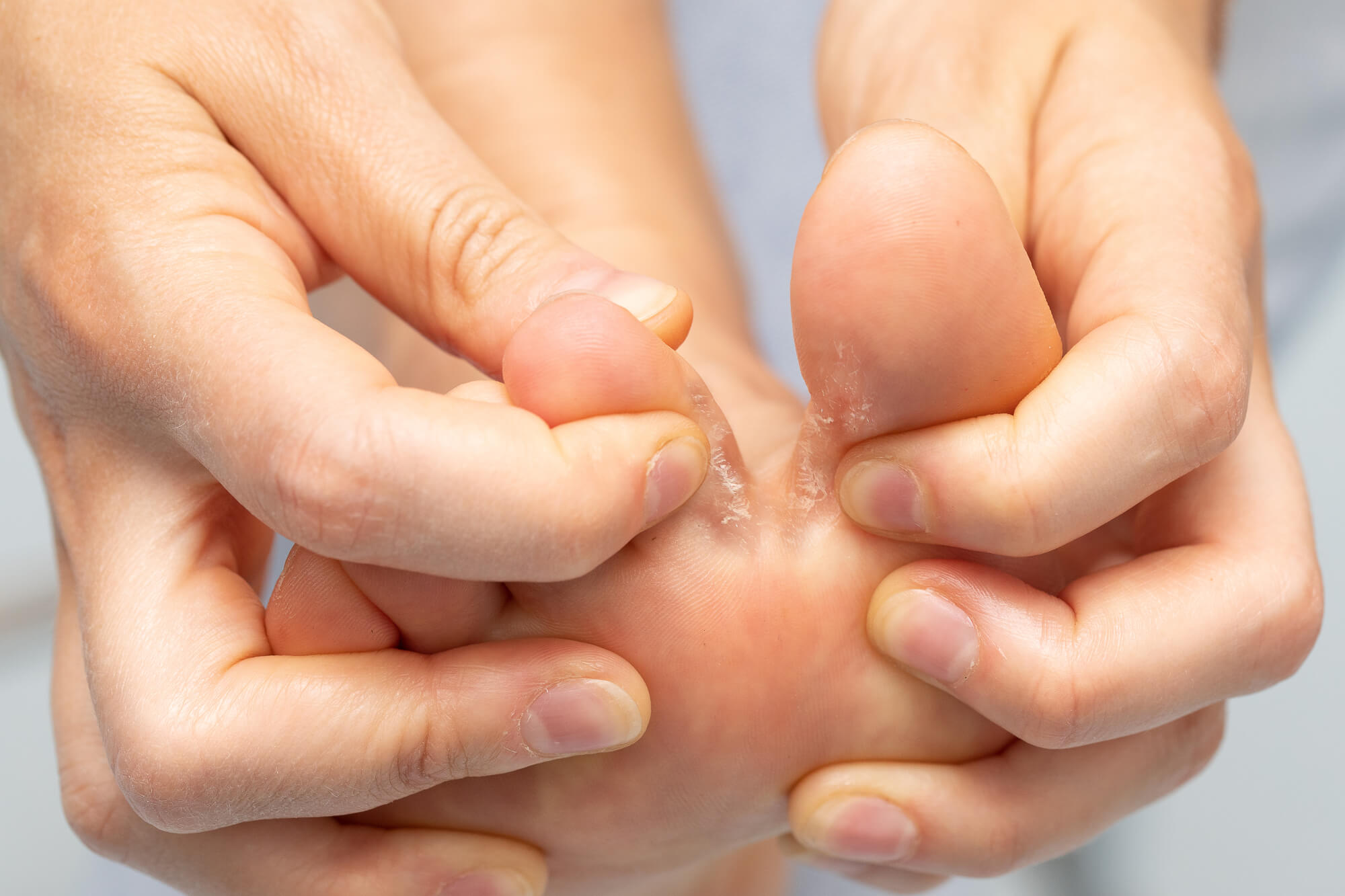
Symptoms of Foot Fungus in People with Diabetes
The symptoms of foot fungus in people with diabetes can be more severe than in people without diabetes. This is because high blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, making it harder for people with diabetes to feel pain or discomfort in their feet. As a result, it can go unnoticed for longer periods of time, leading to more severe infections.
Symptoms in people with diabetes may include:
- Thickened or discolored nails
- Crumbling or brittle nails
- Distorted nail shape
- Foul odor
- Pain or discomfort
- Other potential symptoms
Preventing Foot Fungus in People with Diabetes
Preventing foot fungus in people with diabetes is important to avoid complications such as infection, amputation, and other foot-related problems. To prevent, it's important to practice good foot care, including:
- Washing and thoroughly drying your feet every day
- Wearing clean socks and changing them daily
- Wearing shoes that fit well and are made of breathable materials
- Avoiding going barefoot in public areas
- Getting regular foot exams from a podiatrist
In addition to these tips, it's also important to avoid smoking, which can increase the risk of foot problems and slow down the healing process.
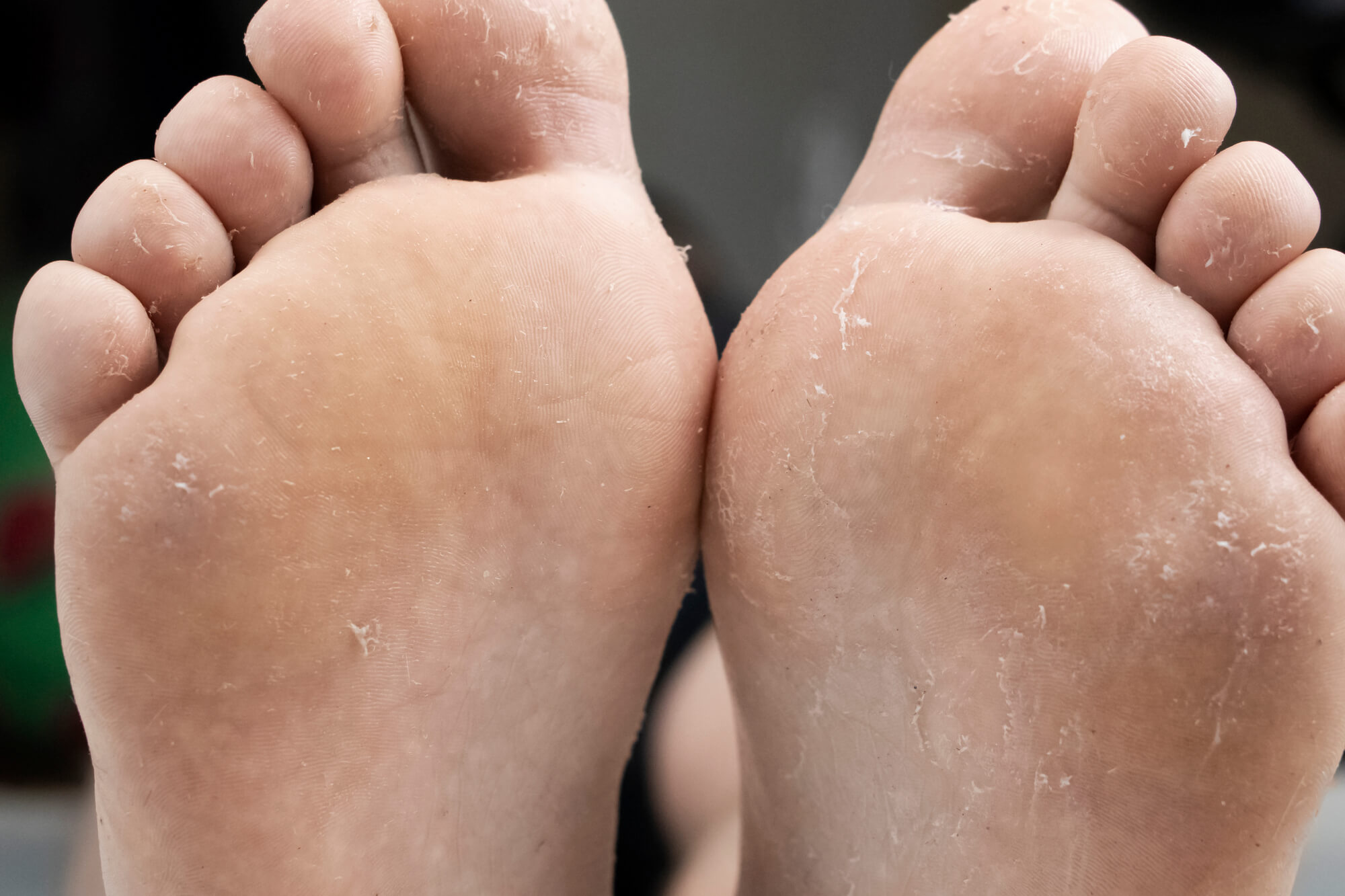

Treating Foot Fungus in People with Diabetes
If you suspect you have foot fungus, it's important to see a podiatrist as soon as possible. A podiatrist can diagnose the type and recommend the best treatment options. Treatment may include:
- Over-the-counter antifungal creams and ointments
- Prescription antifungal medications, such as terbinafine
- Topical antifungal nail lacquer
- Other potential treatment options
It's important to follow your podiatrist's instructions carefully and continue treatment until the foot fungus is completely gone.
When to See a Podiatrist
If you have diabetes, it's important to see a podiatrist regularly to check for signs of foot fungus and other foot-related problems. If you notice any of the symptoms, it's important to see a podiatrist right away to prevent the infection from spreading.
Mild cases may be treatable with over-the-counter remedies, but more severe cases may require prescription medication or other interventions. If you have a history of foot problems or nerve damage, it's especially important to seek medical attention for foot fungus or any other foot-related condition.
Conclusion
Foot fungus is a common condition that can be especially dangerous for people with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. To prevent foot fungus and other foot-related problems, it's important to practice good foot care and see a podiatrist regularly.
If you have diabetes and suspect you have foot fungus, it's important to see a podiatrist as soon as possible. A podiatrist can diagnose the type of foot fungus and recommend the best treatment options for your condition. By taking prevention steps and seeking prompt medical attention for any foot-related concerns, you can protect your feet and maintain good overall health.

