Achilles Tendon Surgery: Everything You Need to Know
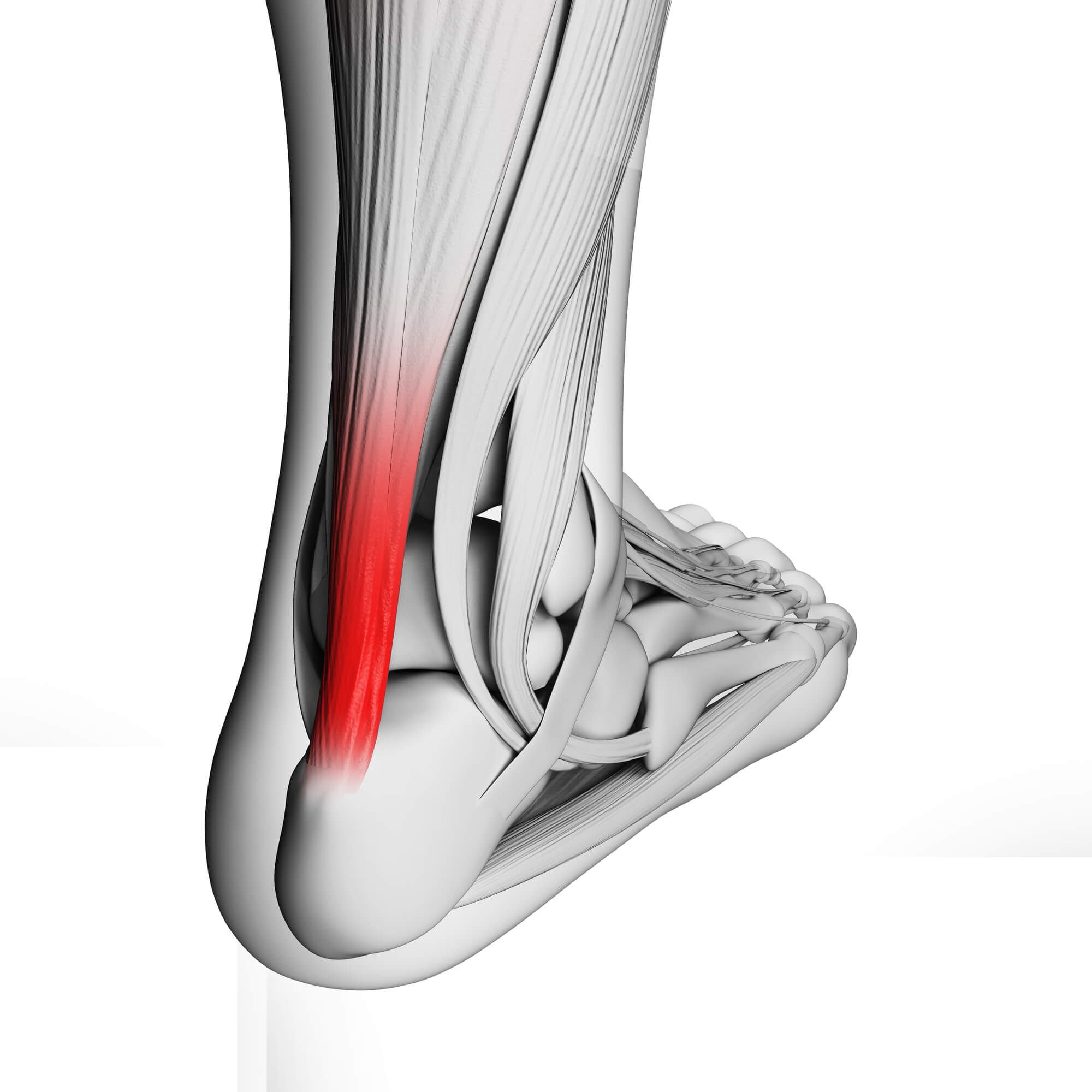
The Achilles tendon is one of the largest tendons in the body, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is responsible for the foot and ankle movement, allowing us to walk, run, jump, and perform various physical activities. However, this strong and resilient tendon can also be vulnerable to injuries, such as tears, ruptures, and other conditions that may require surgery to repair.
Understanding the Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon is located at the back of the lower leg and is responsible for transmitting the force of the calf muscles to the heel bone. This tendon is essential for standing, walking, and running, and it can withstand a significant amount of force. However, repetitive stress, overuse, and sudden trauma can cause damage to the tendon, resulting in pain, swelling, and other symptoms.
Common injuries to the Achilles tendon include tendinitis, tendinosis, partial tears, and complete ruptures. Tendinitis and tendinosis refer to inflammation and degeneration of the tendon, respectively, while partial tears involve damage to a portion of the tendon. On the other hand, complete ruptures refer to a complete tendon tear, which may require surgical intervention.
When is Achilles Tendon Surgery Necessary?
Achilles tendon surgery may be necessary when non-surgical treatment options fail to alleviate the symptoms of a torn tendon. Non-surgical treatments for Achilles tendon injuries include rest, ice, compression, elevation, physical therapy, and immobilization with a cast or brace. However, these treatments may not be effective for severe or chronic injuries, and surgery may be the best option to restore the tendon's function and prevent future injuries.
Achilles tendon surgery may be necessary for the following conditions:
- Complete rupture of the Achilles tendon
- Partial tear of the Achilles tendon that causes significant weakness or pain
- Tendinitis or tendinosis that is unresponsive to conservative treatment
- Chronic Achilles tendonitis that causes persistent pain and swelling
Preparing for Achilles Tendon Surgery
If you and your doctor have decided that Achilles tendon surgery is the best option for your condition, carefully preparing for the procedure is essential. This involves scheduling a pre-operative appointment to review your medical history, undergo a physical examination, and discuss the details of the surgery.
Before the surgery, your doctor may ask you to fast for several hours to prevent complications during the anesthesia. They may also instruct you to stop taking certain medications that interfere with blood clotting, such as aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). You will also need to arrange for transportation to and from the hospital and someone to help you at home during the early stages of recovery.
Types of Achilles Tendon Surgery
There are several types of Achilles tendon surgery, depending on the severity and location of the injury. The two main types of surgery are open surgery and minimally invasive surgery.
Open surgery involves making a large incision in the back of the ankle to access the tendon and repair it using sutures, screws, or other fixation devices. This procedure is typically used for complete ruptures or significant tears requiring more extensive repair.
Minimally invasive surgery, on the other hand, involves making one or more small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments to repair the tendon. This procedure is less invasive than open surgery and may have a shorter recovery time, but it may not be suitable for all types of injuries.
Procedure and Recovery
The procedure for Achilles tendon surgery varies depending on the type of surgery and the extent of the injury. Achilles tendon surgery is performed under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep during the procedure. Your surgeon will make the necessary incision(s) and repair the tendon using sutures or other fixation devices. The surgery typically takes 60-90 minutes, but it may take longer for more severe injuries.
After the surgery, you will be taken to a recovery room and monitored until the anesthesia wears off. You may experience pain, swelling, and bruising in the ankle and calf area, which can be managed with medication and ice packs. You must keep your leg elevated as much as possible and avoid putting weight on the affected leg for several weeks.
The recovery process for Achilles tendon surgery can take several months, depending on the extent of the injury and the type of surgery. During this time, you must follow a rehabilitation program to help you regain strength and flexibility in your ankle and calf muscles. This program may include physical therapy, exercises, and stretches to help you regain mobility and reduce the risk of future injuries.
Risks and Complications
Like any surgery, Achilles tendon surgery carries some risks and potential complications. The most common risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and blood clots. Other potential complications include wound healing problems, scar tissue formation, and prolonged recovery.
To minimize your risk of complications, following your surgeon's instructions carefully, especially regarding wound care and physical activity, is essential. You should also watch for signs of infection, such as fever, swelling, or drainage from the incision site, and contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of these symptoms.
Success Rates and Prognosis
The success rate of Achilles tendon surgery depends on various factors, such as the type and extent of the injury, the type of surgery, and the patient's overall health and compliance with rehabilitation. In general, the success rate of Achilles tendon surgery is high, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in pain, strength, and mobility.
However, the recovery process can be long and challenging, and it may take several months to return to normal activities. It's essential to be patient and follow your rehabilitation program carefully to ensure a successful outcome.
Conclusion
Achilles tendon surgery can be a life-changing procedure for patients with severe or chronic injuries that affect the function of their ankle and calf muscles. By understanding the different types of surgery, preparing carefully for the procedure, and following a rehabilitation program, you can recover from your injury and regain your mobility and quality of life.
If you're experiencing symptoms of an Achilles tendon injury, such as pain, swelling, or weakness, seeking medical attention promptly is essential. A podiatrist or orthopedic surgeon can evaluate your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment options, including surgery if necessary. Taking action early can minimize your risk of complications and improve your chances of a successful recovery.

