Are You Born with Flat Feet?
If you're wondering whether flat feet are something you're born with, the answer is yes and no. While some people are born with flat feet due to genetics or other factors, others may develop flat feet over time due to injury, medical conditions, or natural development. Flat feet, also known as fallen arches, commonly affect adults and children. It refers to the absence of the arch in the foot, which can cause pain and discomfort. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention measures for flat feet.
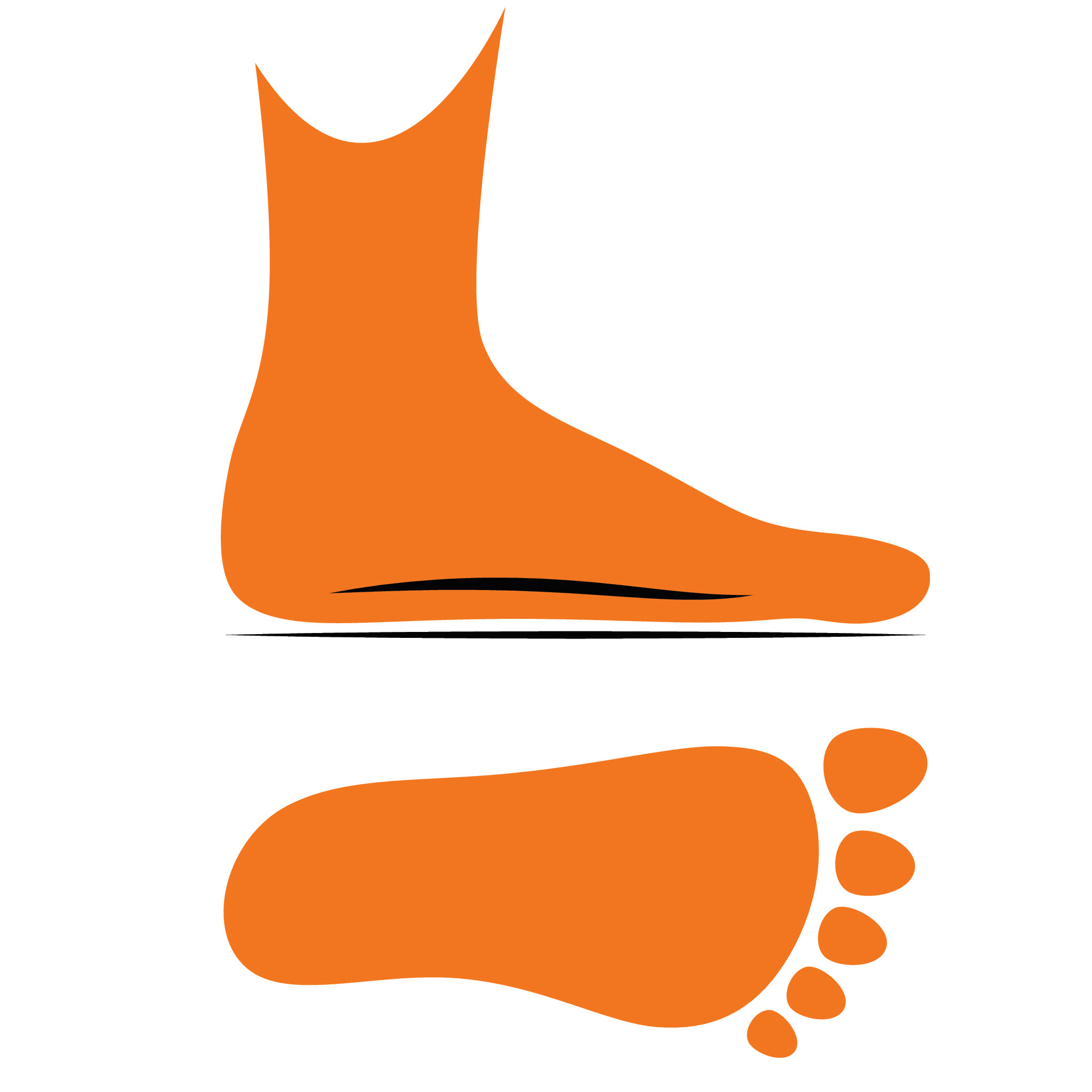
What Are Flat Feet?
Flat feet or fallen arches are a condition where the arch of the foot is absent. The arch of the foot is made up of bones, ligaments, and tendons that work together to provide support and flexibility to the foot. When the arch is absent, the entire foot may touch the ground when walking, causing discomfort and pain.
Causes of Flat Feet
Various factors, including genetics, medical conditions, injury, or natural development, may cause flat feet. Understanding the causes of flat feet can help diagnose and determine the best course of treatment.
Genetics
Flat feet may be hereditary and passed down from generation to generation. Children may inherit flat feet from their parents, making it more likely for them to develop the condition.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can cause flat feet. For example, conditions that affect the muscles or nervous system, such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, can weaken the muscles and tendons in the feet, leading to flat feet. Additionally, arthritis, which causes inflammation and joint pain, can contribute to flat feet.
Injury
Injury to the foot or ankle can damage the tendons that support the arch, leading to flat feet. For example, an injury that damages the tibial tendon, which runs from the ankle to the arch of the foot, can weaken the tendon and cause it to stretch or tear, resulting in flat feet.
Natural Development
In some cases, flat feet may develop naturally over time. This is particularly true in children whose feet are still developing. Infants and toddlers typically have flat feet because their arches have not fully developed yet. Most children develop arches between 3 and 5 years old, but some may not develop them until later. In rare cases, some children may never develop arches, leading to flat feet.
Rigid Flat Feet
In some cases, flat feet may be rigid, which means the foot cannot flex properly. Rigid flat feet are often caused by a bone abnormality or a problem with the ankle joint. Rigid flat feet may present at birth or develop later in life.
Understanding the causes of flat feet is important to determine the most effective treatment options. If you're experiencing foot pain or discomfort, seeking professional advice from a podiatrist is important.
Symptoms of Flat Feet
Flat feet may cause pain or discomfort in the feet, legs, or lower back. The pain may be exacerbated by standing or walking for long periods. Other symptoms may include pronation or other gait abnormalities, the feeling of the foot rolling inwards, and difficulty fitting into shoes.
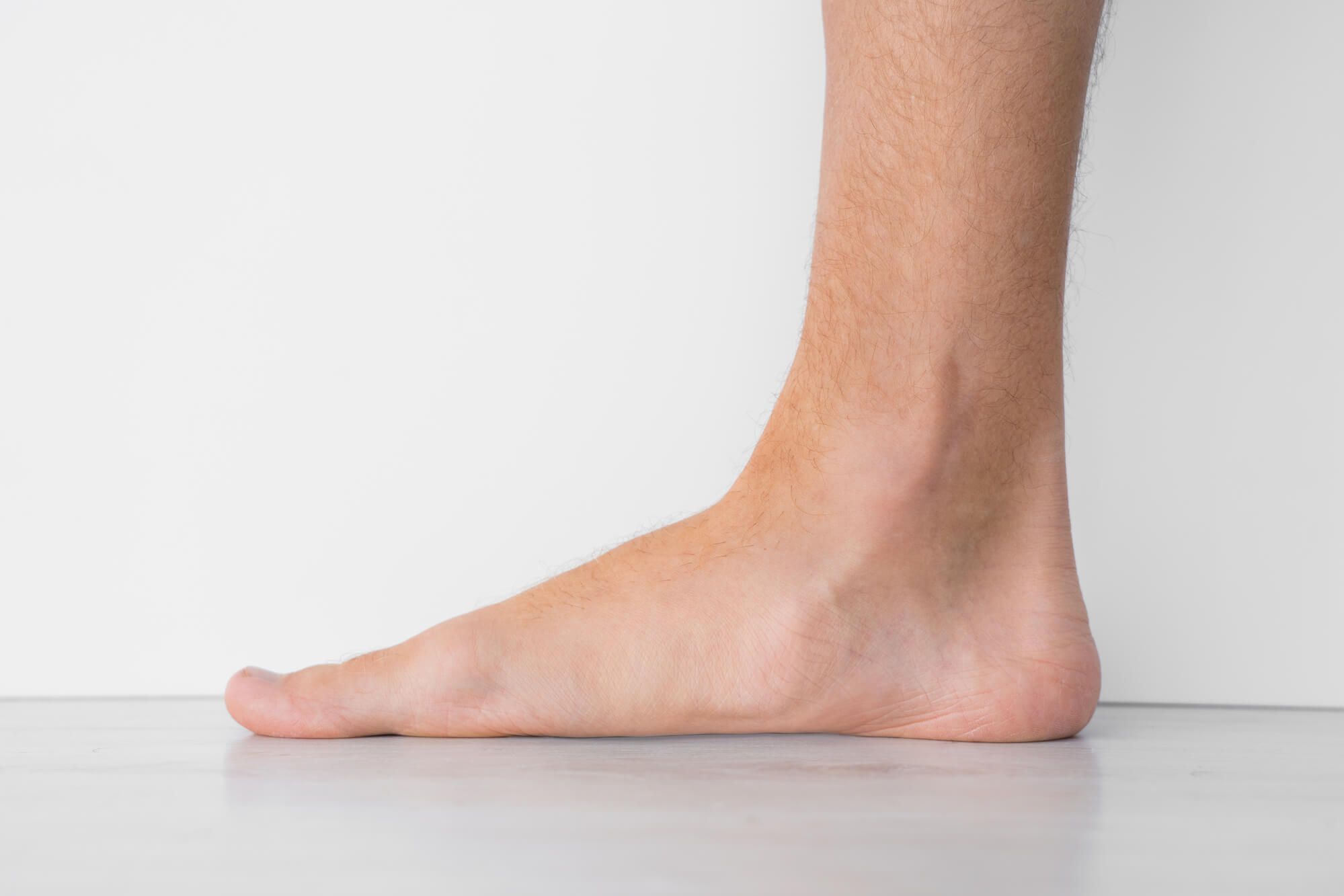
Diagnosis of Flat Feet
A podiatrist can diagnose flat feet by examining the feet and taking an X-ray. The X-ray can show whether the arch is absent or if there are other issues, such as a tibial tendon dysfunction. The podiatrist may recommend further imaging tests or refer the patient to an orthopedic surgeon for further evaluation.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options for flat feet, including orthotic devices, physical therapy, and surgery. Orthotic devices such as custom shoe inserts or arch supports can help alleviate foot pain and improve gait. Physical therapy and exercises can help strengthen the foot and ankle, reducing the risk of injury and preventing further arch collapse. Surgery may be necessary in severe cases where other treatment options are ineffective.
Prevention
Preventing flat feet from developing involves maintaining a healthy weight, wearing supportive shoes, and exercising regularly. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on the feet, while supportive shoes provide stability and cushioning. Exercising regularly can strengthen the muscles in the foot and ankle, reducing the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Flat feet or fallen arches are common conditions that can cause pain and discomfort. While some people are born with flat feet, others develop them due to injury, medical conditions, or other factors. A podiatrist can diagnose and recommend the best treatment options for flat feet. By taking preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing flat feet or prevent them from getting worse.

