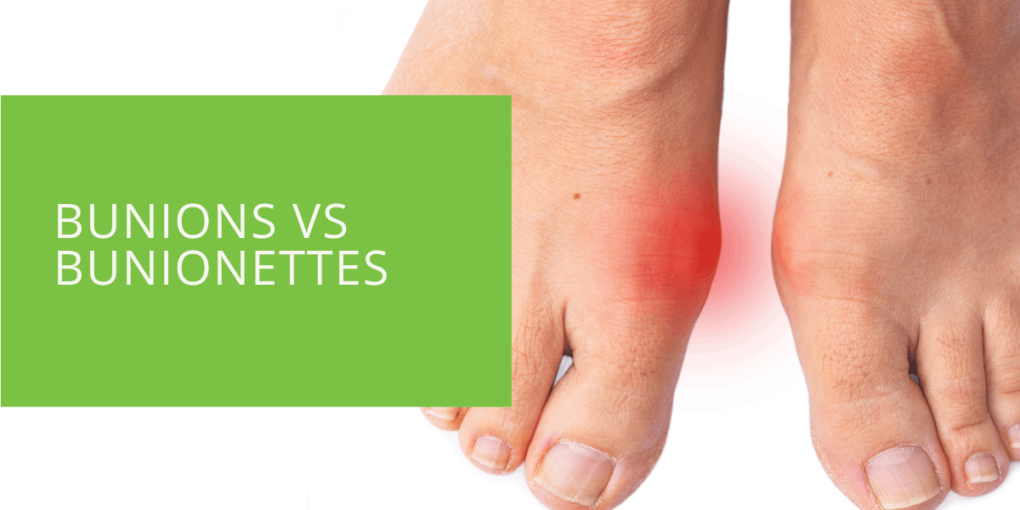
Bunions vs. Bunionettes: Understanding the Differences
Bunions and bunionettes are both foot conditions that can cause pain and discomfort. They are both bony deformities that can be found on the foot. However, they differ in their location, appearance, and severity. This article will discuss the differences between bunions and bunionettes, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What are Bunions and Bunionettes?
Bunions
Bunions, also known as hallux valgus, are a common foot condition that occurs when the big toe pushes against the second toe. This causes the joint at the base of the big toe to stick out and become inflamed. Bunions are typically caused by wearing too tight, narrow, or high shoes. Genetics can also play a role in the development of bunions. Women are more likely to develop bunions than men.
Symptoms of bunions can include pain, redness, and swelling at the base of the big toe. The toe may also become stiff and difficult to move. If left untreated, bunions can cause the foot to become deformed, leading to other foot problems.
Diagnosis of bunions typically involves a physical examination and an X-ray. Treatment options for bunions include wearing wider shoes with a lower heel, using orthotics or shoe inserts, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. Surgery may be necessary if the bunion is severe and causing significant pain or deformity.
Bunionettes
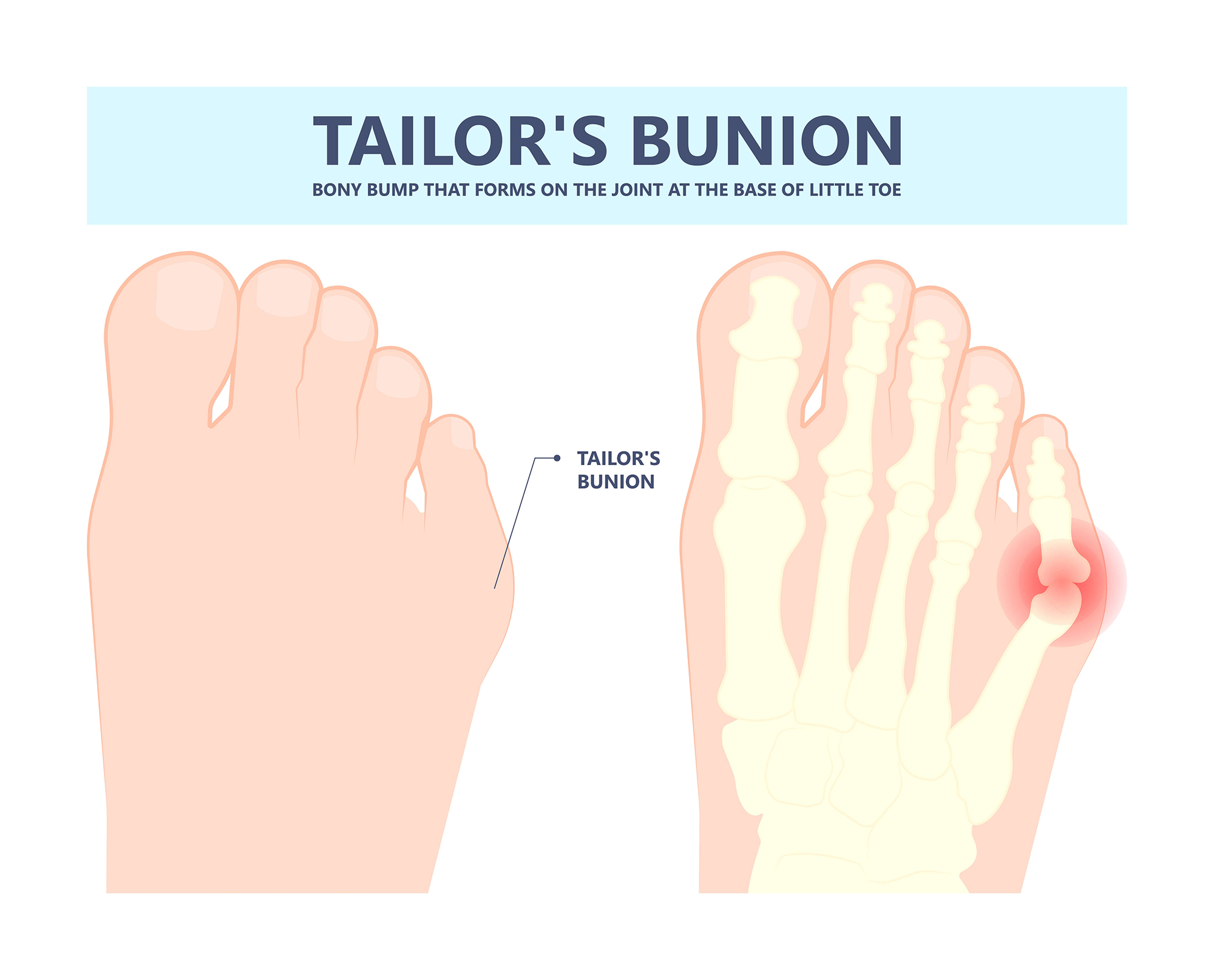
Bunionettes, also known as a tailor's bunion, are similar to bunions but occur outside the foot, near the little toe. A Bunionette is caused by a bony bump on the fifth metatarsal bone, which pushes the little toe toward the other toes. They can be caused by wearing shoes that are too tight or too narrow or by genetics.
Symptoms of bunionettes can include pain, redness, and swelling on the outside of the foot near the little toe. The toe may also become stiff and difficult to move. They can also cause corns or calluses to develop in the affected area.
Diagnosis of bunionettes typically involves a physical examination and an X-ray. Treatment options for a bunionette are similar to those for bunions. They include wearing wider shoes with a lower heel, using orthotics or shoe inserts, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
How are Bunions and Bunionettes Different?
Location
One of the main differences between bunions and bunionettes is their location on the foot. Bunions occur on the inside of the foot, near the big toe, while bunionettes occur on the outside of the foot, near the little toe.
Appearance
Bunions and bunionettes also differ in their appearance. Bunions typically appear as a bony bump on the inside of the foot, near the big toe. Bunionettes, on the other hand, appears as a bony bump on the outside of the foot, near the little toe. The skin over both conditions may become red and inflamed, but bunions are generally larger than bunionettes.
Severity
Bunions and bunionettes can also differ in their severity. Bunions can become quite severe and cause significant pain and deformity. Bunionettes are generally less severe than bunions but can still cause discomfort and limit mobility.
When to See a Podiatrist
If you're experiencing symptoms of bunions or bunionettes, it's important to see a podiatrist. They can diagnose the condition and provide treatment options. Symptoms that indicate a need to see a podiatrist include:
- Pain at the base of the big toe or little toe
- Swelling, redness, or inflammation on the foot
- Difficulty moving the affected toe
- Corns or calluses on the foot
- A visible bump on the inside or outside of the foot
If left untreated, bunions and bunionettes can become more severe, leading to other foot problems. For example, bunions can cause the foot to become misaligned, leading to other conditions such as hammertoe or plantar fasciitis. Bunionettes can also cause the foot to become misaligned, leading to pain and discomfort in the ankle or knee.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for bunions and bunionettes depend on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, non-surgical interventions may be sufficient to relieve pain and discomfort. These can include:
- Wearing wider shoes with a lower heel: Shoes that are too tight or too narrow can aggravate both conditions, so it's important to wear shoes that fit properly.
- Using orthotics or shoe inserts: These can help redistribute pressure on the foot and provide support to the affected area.
- Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve foot mobility and reduce pain.
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to realign the affected toe or remove the bony bump. Surgery for bunions or bunionettes is typically done on an outpatient basis, meaning patients can go home the same day as the procedure. Recovery time can vary depending on the type of surgery performed, but patients can typically expect to return to normal activities within several weeks.
How to Help Prevent Bunions and Bunionettes
While genetics can play a role in the development of bunions and bunionettes, there are several steps you can take to help prevent them from occurring:
- Wear comfortable, supportive shoes: Shoes that fit properly and provide good support can help prevent both conditions from developing.
- Avoid high heels: High heels can pressure the foot and cause the toes to become misaligned.
- Choose shoes with a wide toe box: Too narrow shoes can cause bunions and bunionettes to develop, so it's important to choose shoes with a wide toe box that allows your toes to move freely.
- Stretch and strengthen your feet: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve foot mobility and reduce the risk of developing bunions and bunionettes.
Conclusion
Bunions and bunionettes are common foot conditions that can cause pain and discomfort. While they share some similarities, they differ in location, appearance, and severity. If you're experiencing symptoms of either of these conditions, it's important to see a podiatrist. Treatment options range from non-surgical interventions like orthotics and physical therapy to surgical options like bunionectomy. By taking steps to prevent these conditions from occurring, you can help keep your feet healthy and pain-free.