Bunions: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. This joint, known as the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, is responsible for supporting the weight of the body as we walk, stand, and move. When a bunion forms, it can cause pain and discomfort, making it difficult to walk or stand for long periods. Bunions can also alter the shape of the foot, causing toes to become misaligned and leading to further foot problems.
Symptoms of Bunions
The most obvious symptom of a bunion is the presence of a bony bump on the joint at the base of the big toe. This bump may be painful or tender to the touch and may be accompanied by swelling or redness around the joint. Other common symptoms of bunions include:
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area, especially when walking or standing for long periods
- Changes in the shape of the foot or toes, including misalignment or overlapping of toes
- Difficulty walking or standing comfortably due to pain or discomfort
- The development of calluses or corns on the foot due to rubbing against poorly fitting shoes
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. A podiatrist, or foot doctor, can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
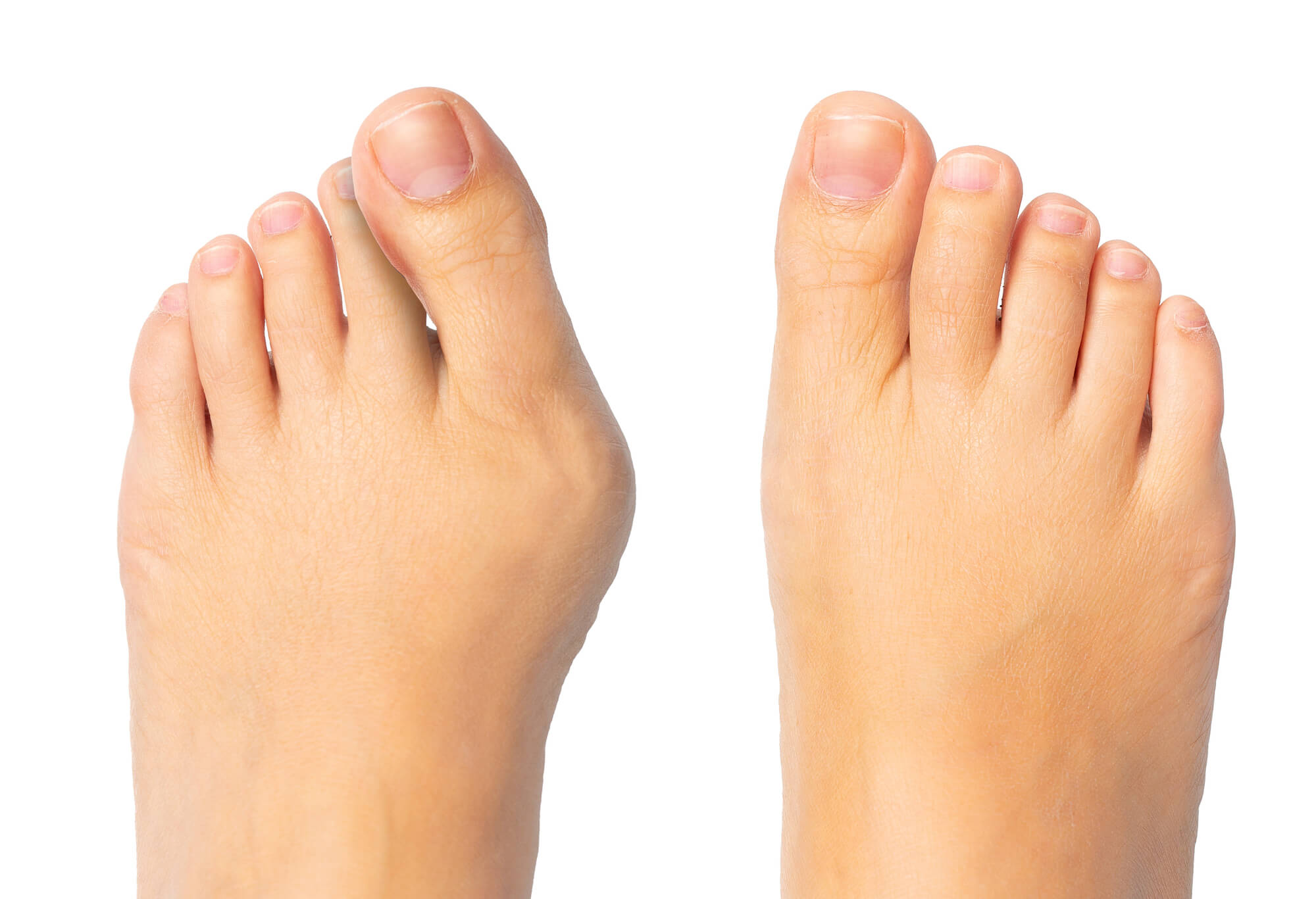
Causes of Bunions
Several factors can contribute to the development of bunions. Some of the most common causes include:
- Genetics and inherited foot structure: Bunions can run in families, suggesting that there may be a genetic component to the condition. If you have a family history of bunions, you may be more likely to develop them yourself.
- Wearing poorly fitting or high-heeled shoes: Shoes that are too tight or have a narrow toe box can put pressure on the MTP joint, leading to the formation of a bunion. High heels can also contribute to bunions' development by shifting the body's weight forward and putting extra strain on the MTP joint.
- Arthritis or other joint conditions: Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause inflammation and damage to the MTP joint, leading to the development of a bunion.
- Trauma or injury to the foot: A foot injury, such as a fracture or sprain, can disrupt the normal alignment of the foot and lead to the formation of a bunion.
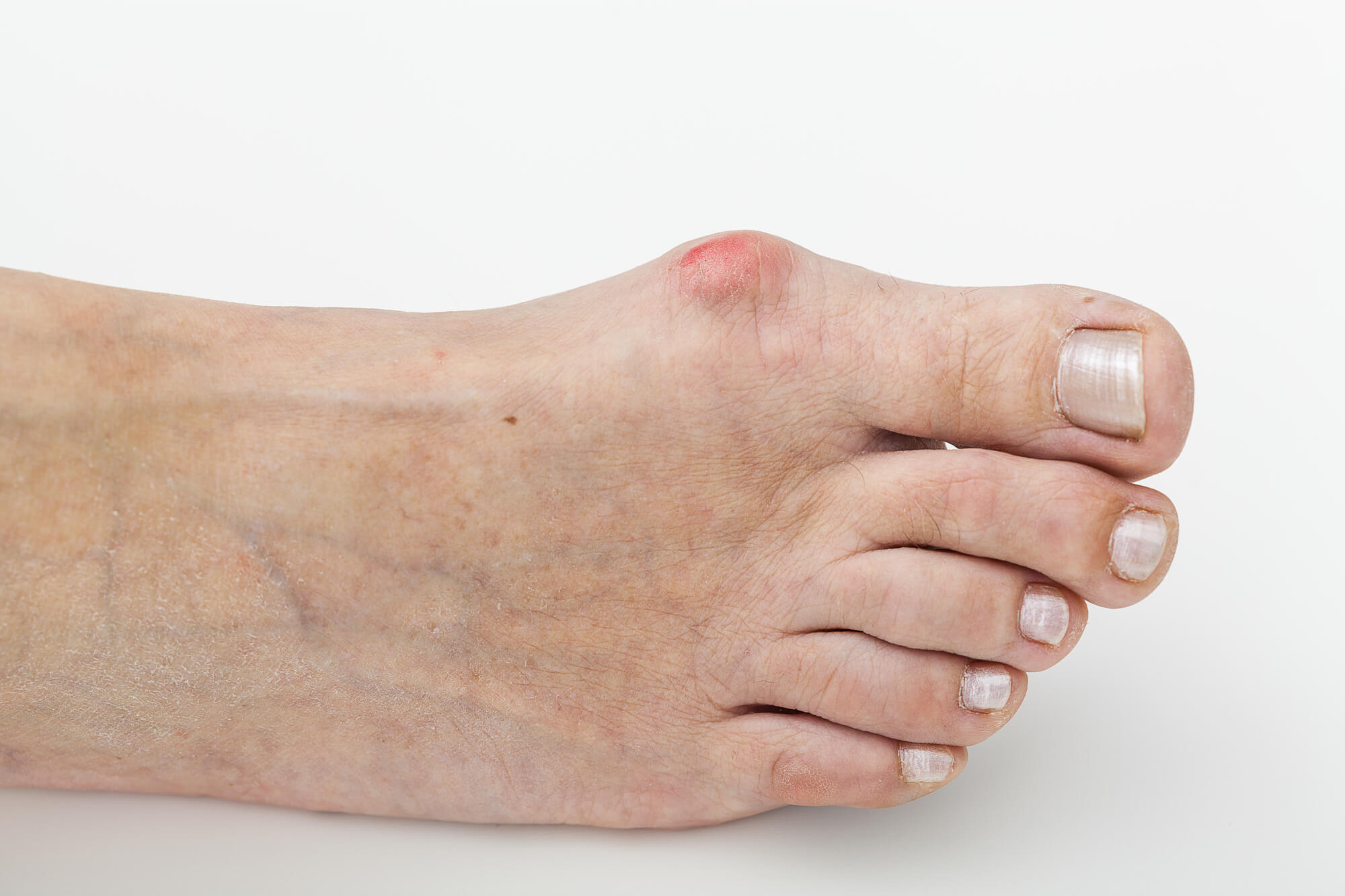
Treatment Options for Bunions
If you have a bunion, there are several treatment options available to help alleviate pain and discomfort. The type of treatment that is best for you will depend on the severity of your condition and your overall health and lifestyle.
Non-surgical Options
For mild to moderate bunions, non-surgical treatment options may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. These options may include the following:
- Wearing comfortable, properly fitting shoes: Choosing shoes that have a wide toe box and provide plenty of room for the toes can help alleviate pressure on the MTP joint and reduce pain. Avoiding high heels and opting for shoes with a low heel can also help.
- Using padding or bunion splints: Padding and splints can help alleviate pressure on the MTP joint and reduce pain. They can also help to realign the toes and improve overall foot function.
- Taking over-the-counter pain medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Resting and icing the affected area: Taking breaks from standing or walking and applying ice to the bunion can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
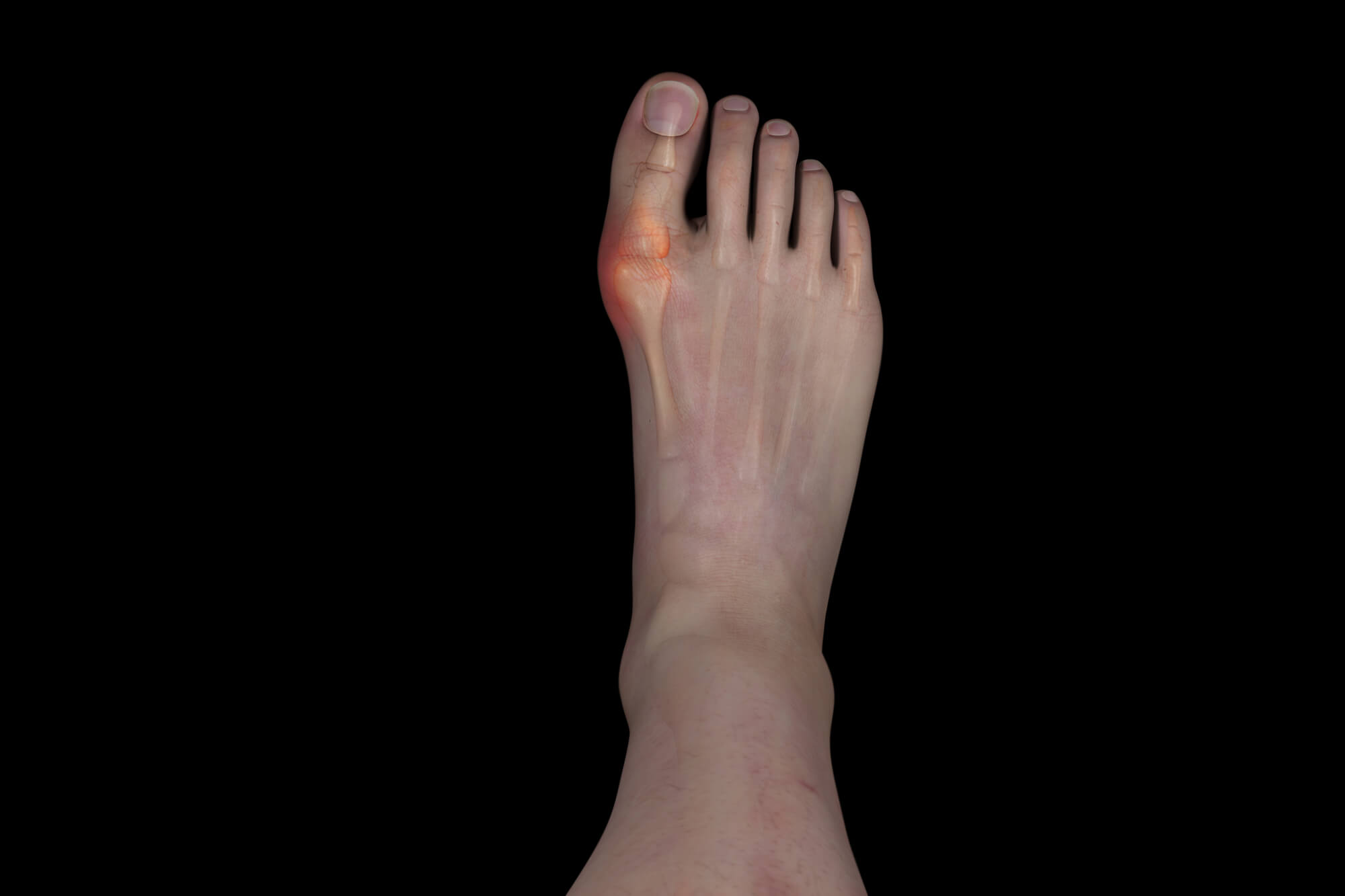
Surgical Options
Surgery may be recommended if non-surgical treatment options are insufficient to alleviate symptoms, or if the bunion is severe. Some common surgical options for bunions include:
- Bunionectomy: During a bunionectomy, the bunion is removed, and the bone is realigned to improve the overall function of the foot. This procedure can be done through a small incision, and recovery time varies depending on the extent of the surgery.
- Osteotomy: An osteotomy involves cutting and realigning the bone to correct the position of the MTP joint. This procedure may be recommended for severe bunions or those with arthritis or other joint conditions.
- Arthrodesis: During an arthrodesis, the MTP joint is fused to reduce pain and improve stability. This procedure may be recommended for those with severe bunions or other joint conditions that have not responded to other treatment options.
Conclusion
Bunions can be painful and impact daily activities, but there are treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve overall foot health. If you are experiencing symptoms of a bunion, it is important to see a healthcare provider, such as a podiatrist, for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations. A podiatrist can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend the best treatment options for you.
Proper footwear and foot care can also help prevent the development of bunions or alleviate existing symptoms. Choosing shoes that fit properly and have a wide toe box can help reduce pressure on the MTP joint and reduce the risk of developing a bunion. Regular stretching and exercises to improve foot flexibility and strength can also help prevent foot problems and maintain overall foot health.
FAQ
What causes bunions?
Bunions can be caused by various factors, including genetics and inherited foot structure, wearing poorly fitting or high-heeled shoes, arthritis or other joint conditions, and trauma or injury to the foot.
What is Hallux Valgus?
Hallux valgus is a deformity of the big toe joint, or metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint, in which the big toe points away from the midline of the body. This deformity is often associated with the development of a bunion.
How do I know if I have a bunion?
Common symptoms of a bunion include pain or discomfort in the affected area, swelling or redness around the joint, difficulty walking or standing for long periods, and changes in the shape of the foot or toes. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Can bunions cause pain in other toes?
Bunions can cause pain in other toes, especially the second toe, which may become bent or overlap with the big toe due to the bunion. This can lead to additional foot problems, such as calluses or corns.
How is a bunion diagnosed?
A bunion is typically diagnosed through a physical examination of the foot. Your healthcare provider may also order an x-ray to better view the bones and joints in your foot. An x-ray can help determine the severity of the bunion and any underlying conditions that may be contributing to its development.
What are the treatment options for bunions?
Treatment options for bunions include non-surgical options, such as wearing comfortable, properly fitting shoes, using padding or bunion splints, taking over-the-counter pain medication, and resting and icing the affected area. Surgical options, such as a bunionectomy, osteotomy, or arthrodesis, may be recommended for severe bunions or those that have not responded to non-surgical treatment.

