Diabetic Foot: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Diabetes foot is a common complication of diabetes that affects the feet and can lead to serious problems if left untreated. People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing foot problems due to poor circulation, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels. People with diabetes need to take proper care of their feet to prevent complications and maintain good foot health. This article will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for diabetes foot and provide tips for maintaining healthy feet with diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes Foot
Several symptoms can indicate the presence of diabetes foot. These include:
- Pain and numbness: Diabetes can cause nerve damage, known as neuropathy, which can lead to pain and numbness in the feet. This can make it difficult to feel if there are any injuries or cuts on the feet, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Swelling: Swelling in the feet and ankles can be a sign of diabetes foot. This can be caused by poor circulation or fluid buildup in the feet.
- Redness and warmth to the touch: Inflammation or infection can cause the skin on the feet to become red and warm to the touch.
- Open sores or wounds that do not heal: Diabetes can impair the body's ability to heal properly, leading to sores or wounds that do not heal. These wounds can become infected if not treated promptly.
- Loss of circulation in the feet: Poor circulation in the feet can lead to a loss of feeling or a tingling sensation. This can make walking difficult and lead to serious complications if left untreated.
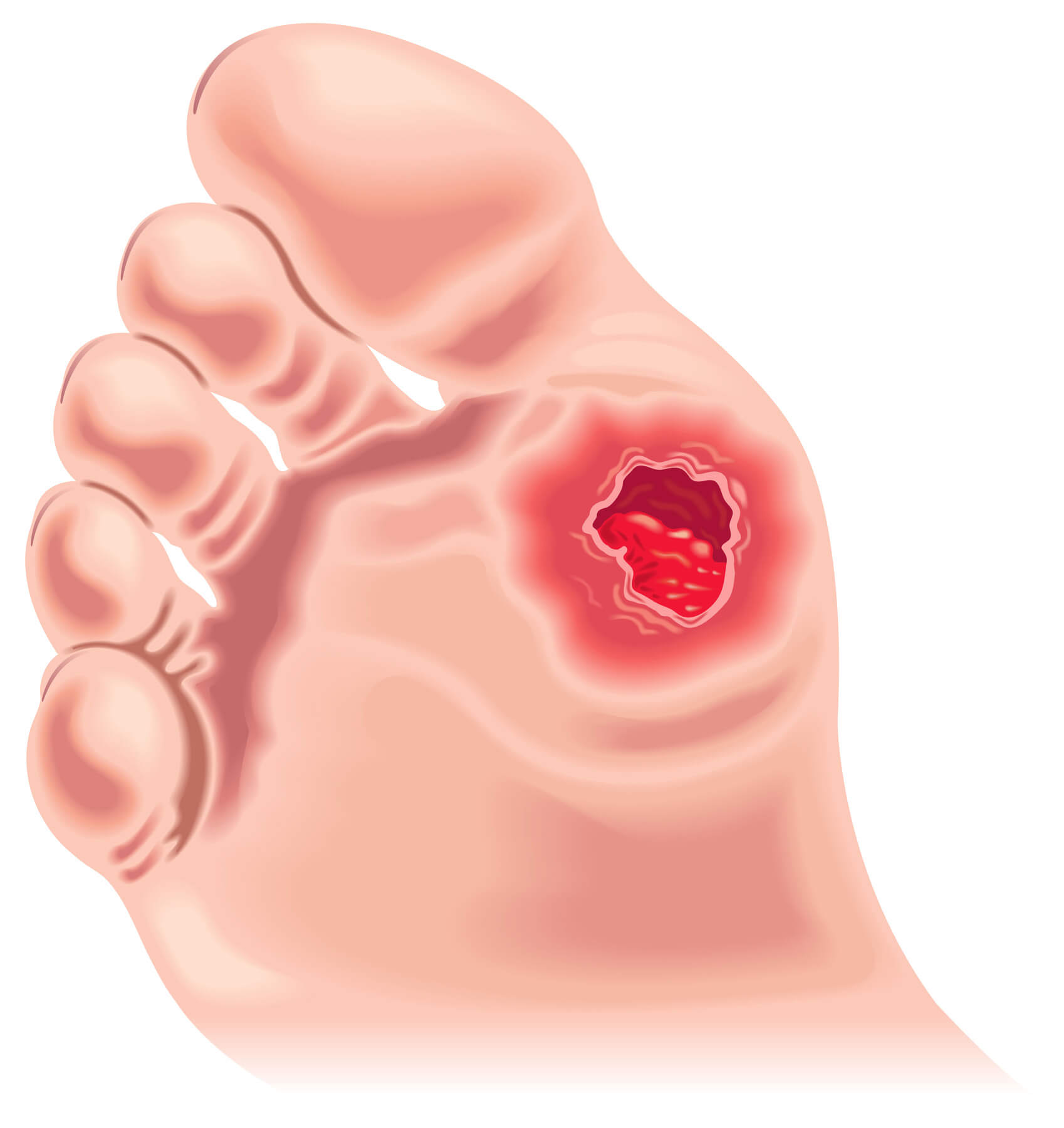
Causes of Diabetes Foot
Several factors can contribute to the development of diabetic foot. These include:
- Diabetes-related nerve damage (neuropathy): Diabetes can cause nerve damage, particularly in the feet. This can lead to a loss of sensation and impaired healing.
- Poor circulation: Diabetes can cause poor circulation in the feet, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients reaching the feet. This can impair healing and increase the risk of infection.
- Infection: People with diabetes are more prone to developing infections, particularly in the feet. This can be due to cuts or wounds that do not heal properly or poor circulation in the feet.
- High blood sugar levels: High blood sugar levels can impair the body's ability to heal and increase the risk of infection.
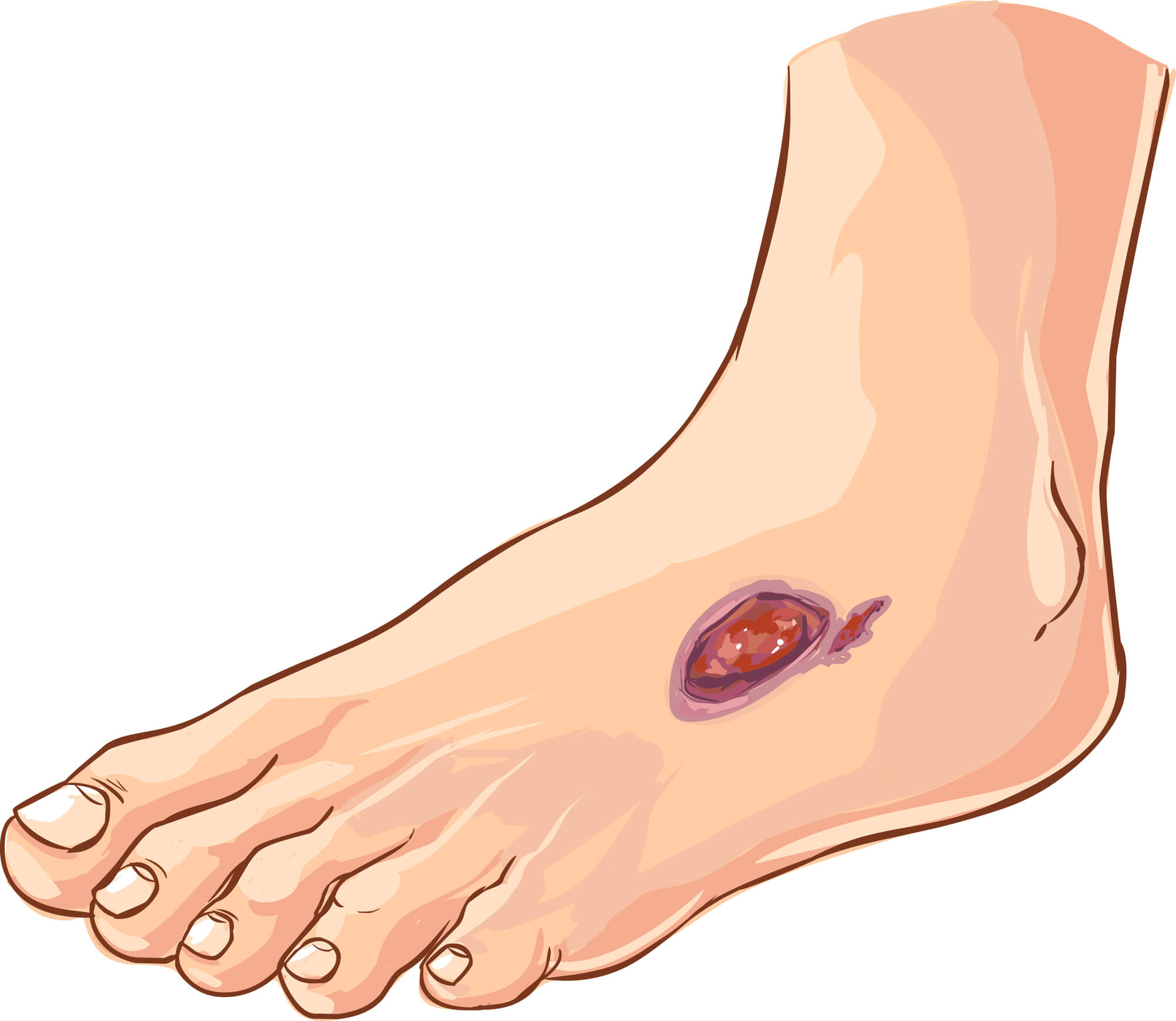
Treatment of Diabetes Foot
Treatment for diabetes foot depends on the severity of the condition and may include:
- Control blood sugar levels: Maintaining good control of blood sugar levels is important for preventing and managing diabetes foot. This can involve following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medications as prescribed.
- Proper foot care: Proper foot care is crucial for preventing and treating diabetes foot. This includes washing and drying the feet thoroughly, trimming toenails carefully, and wearing well-fitting shoes that provide proper support. Inspecting the feet daily for any cuts, sores, or other problems is also important.
- Medications: Depending on the cause of the diabetes foot, medications may be prescribed to help manage pain, reduce inflammation, or treat infections.
- Surgery (in severe cases): In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat diabetes foot, particularly if some open sores or wounds are not healing.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve circulation and strengthen the muscles in the feet.
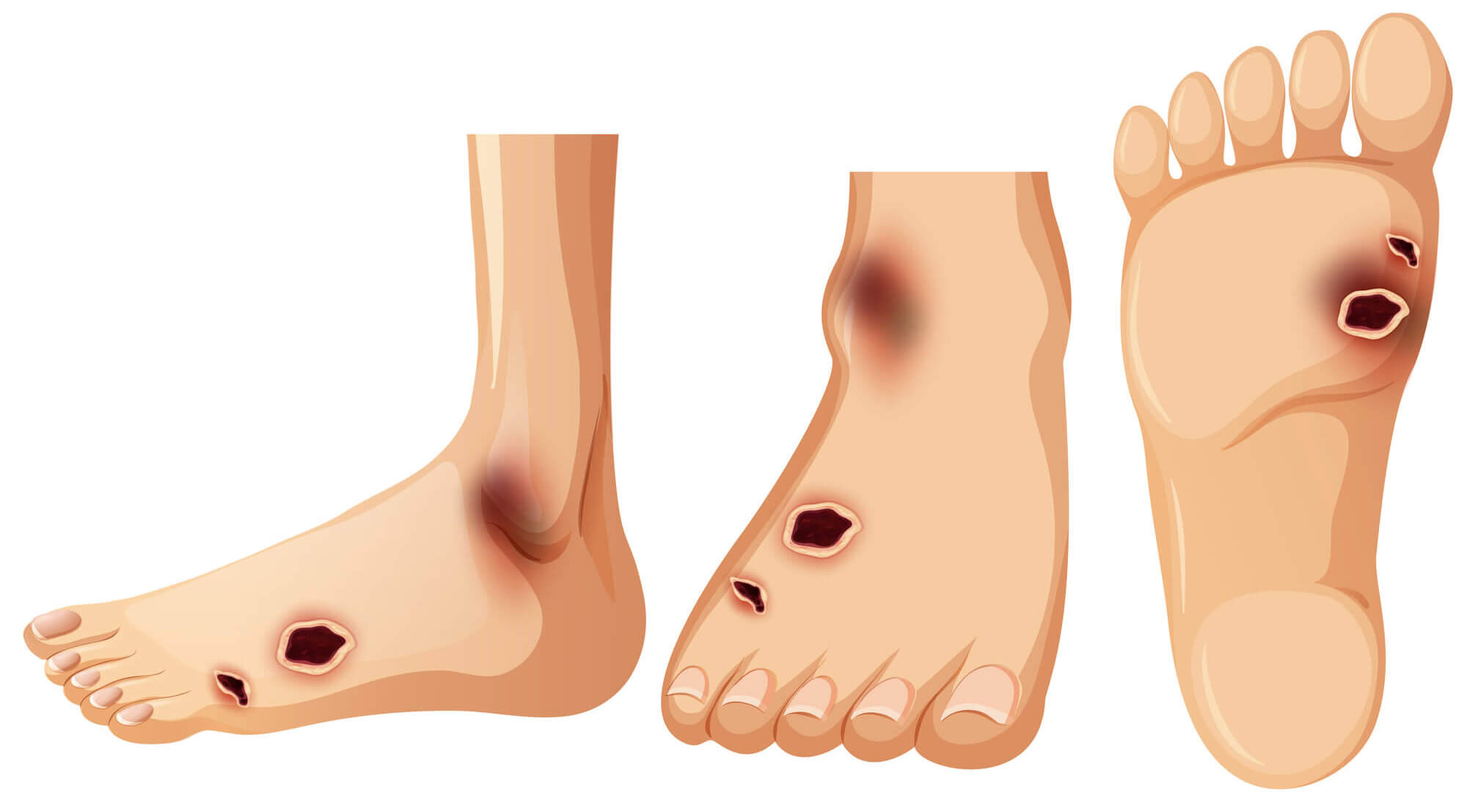
Conclusion
Diabetes foot is a common complication of diabetes that can lead to serious problems if left untreated. People with diabetes need to pay attention to the health of their feet and seek medical attention if they experience any of the symptoms listed above. By maintaining good control of blood sugar levels, practicing proper foot care, and seeking medical treatment, people with diabetes can prevent and manage foot problems and maintain healthy feet.
If you are concerned about diabetes foot or have any questions about how to care for your feet, it is recommended to consult with a podiatrist or other healthcare professional. Podiatrists are trained to diagnose and treat foot problems and can provide guidance on preventing complications and maintaining good foot health.
FAQ
What is a foot ulcer, and how is it related to diabetes?
A foot ulcer is an open sore or wound on the foot that is difficult to heal. People with diabetes are more prone to developing foot ulcers due to poor circulation and nerve damage, impairing the body's ability to heal properly. Foot ulcers can be caused by injuries, cuts, or pressure on the feet, and if left untreated, they can lead to serious complications.
How can I prevent foot ulcers and other foot complications related to diabetes?
There are several steps you can take to protect your feet and prevent foot complications related to diabetes:
- Check your feet every day: Inspect your feet daily for any cuts, sores, or other problems. Use a mirror to check the bottoms of your feet if it is difficult to see them.
- Keep your blood sugar levels in check: Maintaining good control of your blood sugar levels can help prevent foot complications. This may involve following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking medications as prescribed.
- Wear shoes that fit properly: Wearing shoes that fit well and provide proper support can help prevent injuries and pressure on the feet.
- Avoid going barefoot: Always wear shoes to protect your feet from injuries and infections.
- Practice good foot hygiene: Wash and dry your feet thoroughly, trim your toenails carefully, and use moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated.
- See a podiatrist regularly: A podiatrist can help you manage foot problems and provide guidance on preventing complications.
What is diabetic neuropathy, and how does it affect the feet?
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur in people with diabetes. It is caused by high blood sugar levels damaging the nerves, particularly in the feet. Diabetic neuropathy can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet, impaired healing, and an increased risk of infection.
What should I do if I think I have a foot infection?
If you have a foot infection, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Foot infections can be serious and can spread quickly if not treated promptly. Your healthcare provider can diagnose the infection and provide treatment to help clear it up. It is also important to practice good foot hygiene and avoid going barefoot to prevent the risk of infection.
How can I improve blood flow to my feet?
There are several steps you can take to improve blood flow to your feet:
- Exercise regularly: Exercise can help improve circulation and strengthen the muscles in your feet.
- Elevate your feet: Elevating your feet above the level of your heart can help improve circulation.
- Wear compression socks: Wearing compression socks can help improve circulation and reduce swelling in the feet.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can damage blood vessels and impair circulation.
How often should I check my feet?
It is recommended to check your feet daily for any cuts, sores, or other problems. If you have difficulty seeing your feet or have foot problems, it may be helpful to use a mirror to check the bottoms of your feet. If you notice any problems, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.

