Tips for Foot Wound Care: How to Promote Healing and Prevent Infection
Foot wounds are common and can be caused by many things, such as cuts, scrapes, blisters, and sores. For people with diabetes, foot wounds can be particularly dangerous because they can lead to ulcers that can become infected and even lead to amputation. Proper wound care is essential for promoting healing and reducing the risk of infection. In this article, we will discuss some tips for foot wound care.
Step-by-Step Guide to Foot Wound Care
Step 1: Clean the Wound
Cleaning a foot wound is the first step in promoting healing and preventing infection. Start by washing your hands with soap and water to avoid introducing new bacteria to the wound. Then, use clean water to rinse the wound and remove dirt or debris. If there is any bleeding, apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth until it stops. Use sterile saline or hydrogen peroxide to help clean a deeper wound. Avoid using alcohol, iodine, or other harsh chemicals that can damage healthy tissue. Once the wound is clean, gently pat it dry with a clean towel.
Step 2: Dress the Wound
After cleaning the wound, the next step is to dress it properly. The type of dressing will depend on the size and location of the wound. For small wounds, a bandage or adhesive strip may be enough. For larger wounds, a sterile gauze pad and tape may be necessary. Changing the dressing daily or more frequently if it becomes wet or dirty is important. When changing the dressing, inspect the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. If you notice any signs of infection, contact your podiatrist immediately.
Step 3: Protect the Wound
Once the wound is clean and dressed, it is important to protect it from further injury. Depending on the location of the wound, a bandage, cast, or splint may be necessary. Avoid putting pressure on the wound or exposing it to friction or rubbing. For example, if the wound is on the sole of your foot, wearing comfortable shoes that fit well is essential to protect it. If you have a diabetic foot ulcer, your podiatrist may recommend special shoes or inserts to help distribute pressure more evenly.
Step 4: Monitor the Wound
After caring for the wound, monitoring it for any changes is important. Look for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, discharge, or foul odor. Other signs to watch for include increased pain, fever, or a change in the color or texture of the wound. If you notice any of these signs, contact your podiatrist immediately. They may prescribe an antibiotic or other medication to prevent or treat an infection.
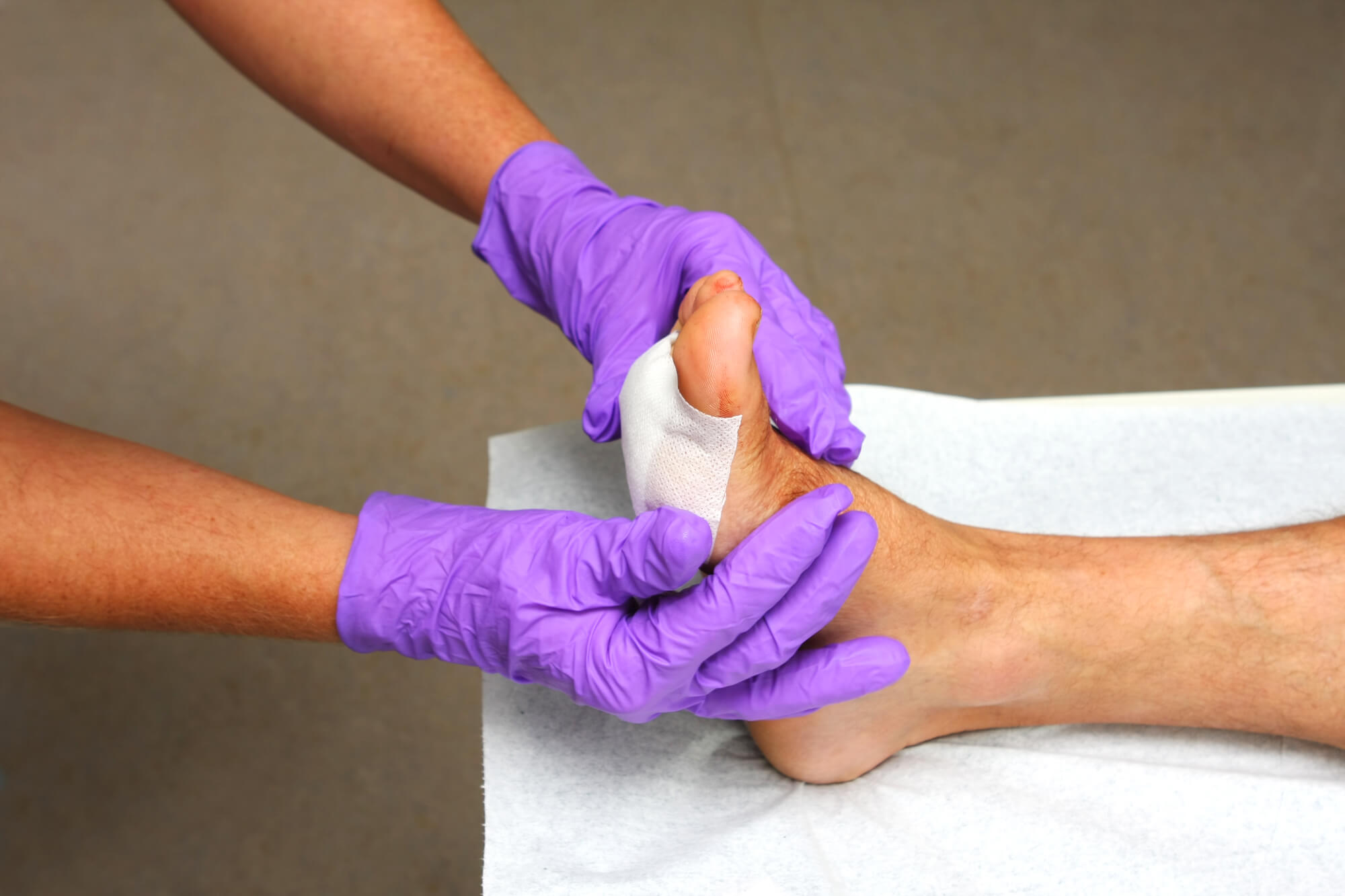
Tips for Preventing Foot Wounds
Preventing foot wounds is key to avoiding the risk of infection and other complications. Here are some tips for preventing foot wounds:
Tip 1: Wear Proper Footwear
Wearing proper footwear is essential for preventing foot wounds. Make sure your shoes fit well and are comfortable. Avoid high heels or shoes that are too tight. If you have diabetes, it is important to wear shoes specifically designed for diabetic feet.
Tip 2: Practice Good Foot Hygiene
Maintaining good foot hygiene is another way to prevent foot wounds. Wash and dry your feet daily, particularly the area between your toes. Moisturize your feet to prevent dry skin that can lead to cracks or fissures.
Tip 3: Check Your Feet Regularly
Checking your feet regularly is important for identifying any potential issues before they become serious. Look for signs of redness, swelling, or bruising. Inspect the soles of your feet and between your toes for any signs of blisters or sores. If you have difficulty seeing the bottom of your feet, use a mirror or ask a family member for help. Remember, early detection of foot wounds is key to preventing complications.
Types of Foot Wounds and Their Causes
Various factors can cause foot wounds, which can be classified into different types depending on their location and severity. Here are some common types of foot wounds and their causes:
- Blisters: Blisters are fluid-filled pockets on the skin due to friction or pressure. Ill-fitting shoes, repetitive motion, or intense physical activity commonly cause them. Blisters can become painful and lead to infection if not properly treated.
- Sores: Sores are open wounds caused by cuts, scrapes, or puncture wounds. They can be caused by stepping on a sharp object, wearing improper footwear, or skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis. Sores can become infected if not properly cleaned and dressed.
- Ulcers: Ulcers are deep, open wounds caused by poor circulation, diabetes, or other medical conditions. They are commonly located on the bottom of the foot and can be difficult to heal. If left untreated, ulcers can lead to serious complications, including infection and amputation.
- Bruises: Bruises are caused by skin and underlying tissue trauma, resulting in discoloration and pain. They can be caused by stubbing your toe, dropping a heavy object on your foot, or other physical injuries. Bruises usually heal independently, but severe bruising can lead to more serious complications.
Conclusion
Foot wound care is essential for promoting healing and preventing infections. Proper wound care includes cleaning the wound, dressing it properly, protecting it from further injury, and monitoring it for any changes. In addition, preventing foot wounds is important for reducing the risk of infection and other complications. Following these tips can help you keep your feet healthy and avoid potential issues. If you have diabetes or are at a higher risk for foot wounds, consult your podiatrist for more information on foot care. Remember, taking care of your feet is important to overall health and well-being.