Ice or Heat for Treating Tendon Pain?
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a common condition affecting countless individuals, causing discomfort, pain, and stiffness in various body parts. Whether you're dealing with acute or chronic tendonitis, finding the right method to alleviate the pain is crucial for a swift recovery. This comprehensive guide will explore the age-old debate: ice or heat? Which of these two remedies is more effective in treating tendon pain and promoting healing?
Key Takeaways
- Choosing between ice and heat therapy for tendonitis depends on factors like pain severity, injury stage, and personal preference.
- Ice therapy effectively reduces inflammation and numbs acute pain, while heat therapy promotes relaxation, increases blood flow, and is better suited for chronic discomfort.
- For personalized advice on tendon pain relief, it's advisable to consult with a podiatrist to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Understanding Tendonitis
What Is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis, often referred to as tendinitis, occurs when tendons, the tough fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, become inflamed or irritated. Various factors, including overuse, repetitive motions, and aging can trigger this condition. Tendonitis commonly affects areas like the elbows, shoulders, and Achilles tendon, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
Symptoms of Tendonitis
Recognizing the signs of tendonitis is the first step toward effective treatment. Typical symptoms include:
- Pain and Swelling: Tenderness around the affected area, often accompanied by swelling.
- Acute Discomfort: Sharp or burning pain, particularly during movement.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and joint stiffness.
- Overuse Connection: Tendonitis is often linked to overuse or excessive strain on a particular tendon.
Tendonitis Pain Relief Methods
Managing Acute Tendonitis Pain
When tendonitis pain strikes suddenly and severely, immediate relief is a top priority. The acronym R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can be a valuable guide in such cases.
Ice: A Cold Comrade
- When to Use Ice: Apply ice immediately after an acute tendon injury.
- How Ice Works: Ice helps reduce inflammation, numb pain, and constrict blood vessels, which can prevent further swelling.
- Using Ice for Achilles Tendonitis: Targeting this area can alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
- The Role of Ice Packs: Applying an ice pack directly to the affected area is a common and effective method.
Rest and Compression
- Rest: Give your affected tendon a break by avoiding activities aggravating the pain.
- Compression: Use bandages or wraps to provide gentle pressure, reducing swelling.
Elevation
- Elevating the Injured Area: Keeping the affected limb elevated can aid in reducing swelling and promoting blood flow.
Treating Chronic Tendonitis
For chronic or long-term tendonitis pain, a different approach may be necessary. Heat therapy can be particularly beneficial in such cases.
The Role of Ice in Tendonitis Treatment
When to Use Ice
Proper timing and application of ice are crucial for its effectiveness in treating tendonitis. Applying ice within 48 hours after an acute injury can significantly reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
How Ice Works
Ice has several mechanisms of action that make it an excellent choice for immediate tendon pain relief. It helps by:
- Reducing Inflammation: Ice constricts blood vessels, reducing the flow of blood to the affected area and minimizing swelling.
- Numbing Pain: Cold temperatures temporarily numb the nerve endings, relieving pain.
- Decreasing Metabolic Activity: Cold reduces metabolic demands, which can help relax muscles and tissues.
Using Ice for Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis, a common form of tendonitis, often requires specialized care. Applying ice directly to the Achilles tendon can effectively manage pain and swelling.
Preventing Tendonitis with Ice
Prevention is key, especially for those at risk of recurrent tendonitis due to specific activities or sports. Incorporating ice therapy into your routine can be a proactive measure.
Applying Heat for Tendon Pain
When Heat Is Beneficial
Heat therapy is generally more suitable for chronic or long-term tendonitis pain, where inflammation is less of an immediate concern.
Heat for Pain Relief
Heat therapy works differently from ice, promoting relaxation, increasing blood flow, and easing stiffness in the affected area. The benefits of heat include:
- Promoting Blood Flow: Heat encourages blood vessels to dilate, improving circulation to the injured area.
- Muscle Relaxation: Heat helps relax muscles, reducing tension and discomfort.
- Easing Stiffness: Applying heat can significantly improve flexibility and range of motion.
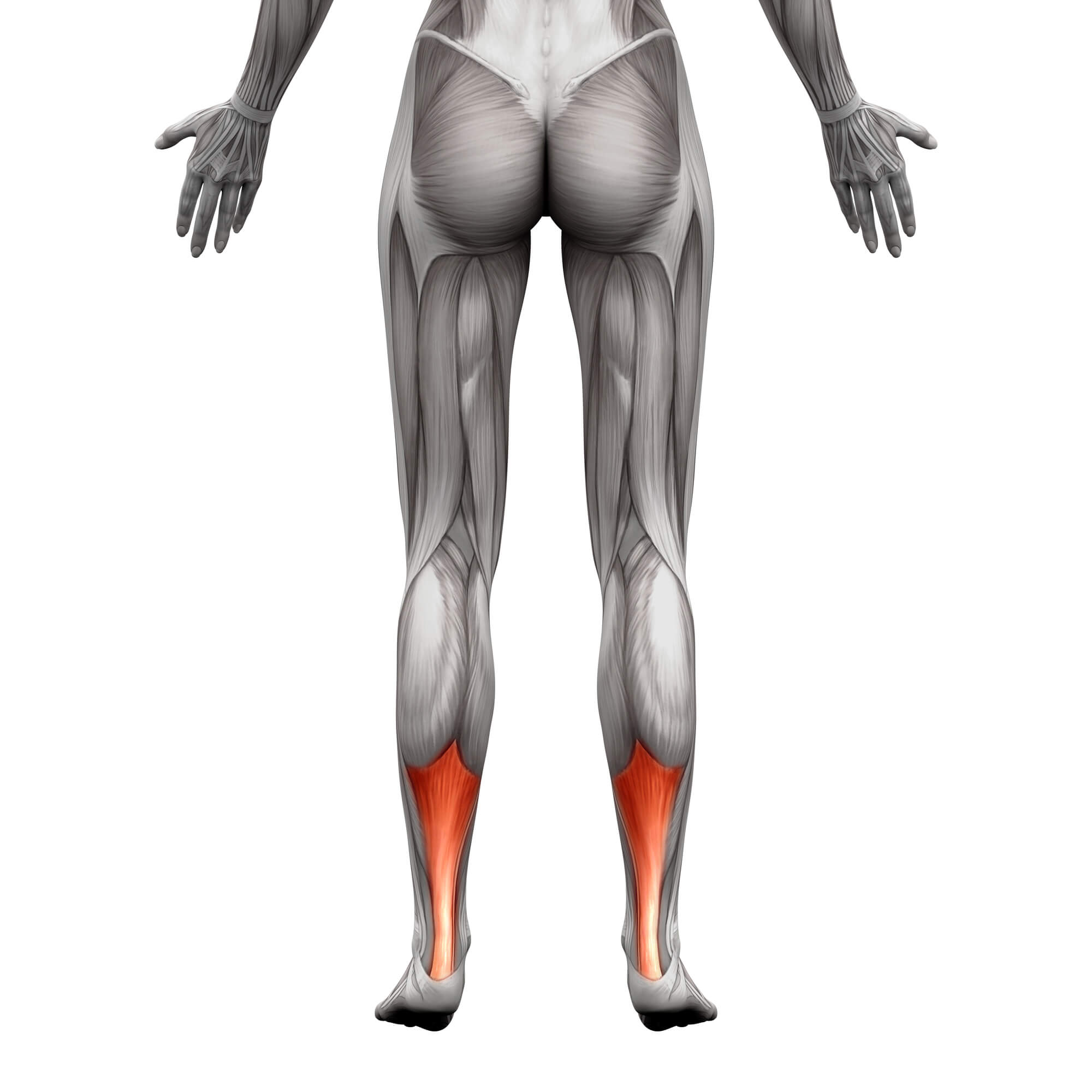
Heat Application for Achilles Tendonitis
When dealing with Achilles tendonitis, targeted heat therapy can be incredibly soothing. It relaxes the calf muscles and increases blood flow to the area, promoting healing.
Using Heat to Prevent Tendonitis
Incorporating heat into your routine can be a preventive measure against tendonitis, particularly if you engage in activities that may increase your risk of developing this condition.
Ice vs. Heat: Choosing the Right Approach
The decision between ice and heat therapy depends on various factors, including the severity of your pain, the acuteness of the injury, and your personal preference.
Factors to Consider
When making this choice, consider the following:
- Severity of Pain: Ice is often recommended for acute, severe pain, while heat may be more appropriate for chronic discomfort.
- The acuteness of Injury: In the early stages of tendonitis or immediately following an injury, ice can help minimize inflammation. Heat is better for ongoing pain relief.
- Personal Preference: Some individuals find one method more soothing than the other. Experiment to see which works best for you.
Combining Ice and Heat
Sometimes, alternating between ice and heat therapy can yield the best results. This approach, known as contrast therapy, involves using both treatments to leverage their unique benefits.
Consulting a Podiatrist
For persistent or severe tendonitis, it's advisable to seek the expertise of a podiatrist or a medical professional. They can provide a tailored treatment plan to address your specific needs.
Conclusion
In tendonitis treatment, ice, and heat therapy are not one-size-fits-all. Each method has its place, depending on the nature and stage of your tendonitis. At ePodiatrists, we understand the complexities of tendon pain, and our expert podiatrists are here to guide you through the best course of action.
We recommend a thoughtful approach to tendonitis management. Whether ice to reduce inflammation or heat to ease chronic discomfort, finding the right balance is essential for a swift recovery. If you're unsure which method is best for your tendonitis or if your symptoms persist, don't hesitate to schedule an appointment with our experienced podiatrists. Your journey to tendonitis relief starts here.

