Magnesium for Plantar Fasciitis: Exploring the Benefits and Uses
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition characterized by heel pain and inflammation of the plantar fascia. While traditional treatments focus on stretching, physical therapy, and orthotics, there is growing interest in alternative approaches. One such approach is using magnesium, a mineral known for its role in various bodily functions. In this article, we will explore the potential benefits of magnesium for plantar fasciitis relief, its food sources, and proper usage guidelines.
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed and irritated. This can lead to intense heel pain, especially with the first steps in the morning or after prolonged rest periods. The condition is often associated with activities that stress the feet, improper footwear, and certain risk factors.
The Importance of Magnesium for Foot Health
Magnesium is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in the body, including muscle and nerve function, energy production, and bone health. It is also involved in maintaining the health of the plantar fascia and the surrounding foot muscles. Adequate magnesium levels are essential for proper muscle contraction, relaxation, and the prevention of cramps.
The Link Between Magnesium Deficiency and Plantar Fasciitis
Understanding Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is essential in various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve function, energy production, and bone health. However, many individuals may experience magnesium deficiency without even realizing it. Factors such as poor diet, certain medications, medical conditions, and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium Deficiency and Inflammation
Plantar fasciitis is characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. Magnesium deficiency has been linked to increased inflammation in the body. When magnesium levels are inadequate, the body's ability to regulate and control inflammation may be compromised. This can contribute to the chronic inflammation observed in plantar fasciitis, exacerbating pain and delaying healing.
Impaired Healing and Magnesium Deficiency
One of the challenges in plantar fasciitis is the impaired healing process of the damaged plantar fascia. Magnesium deficiency can interfere with the body's ability to repair and regenerate tissues. Adequate magnesium levels are necessary for collagen synthesis, a crucial component of tissue repair. Without sufficient magnesium, the healing process may be slowed, leading to prolonged pain and discomfort in individuals with plantar fasciitis.
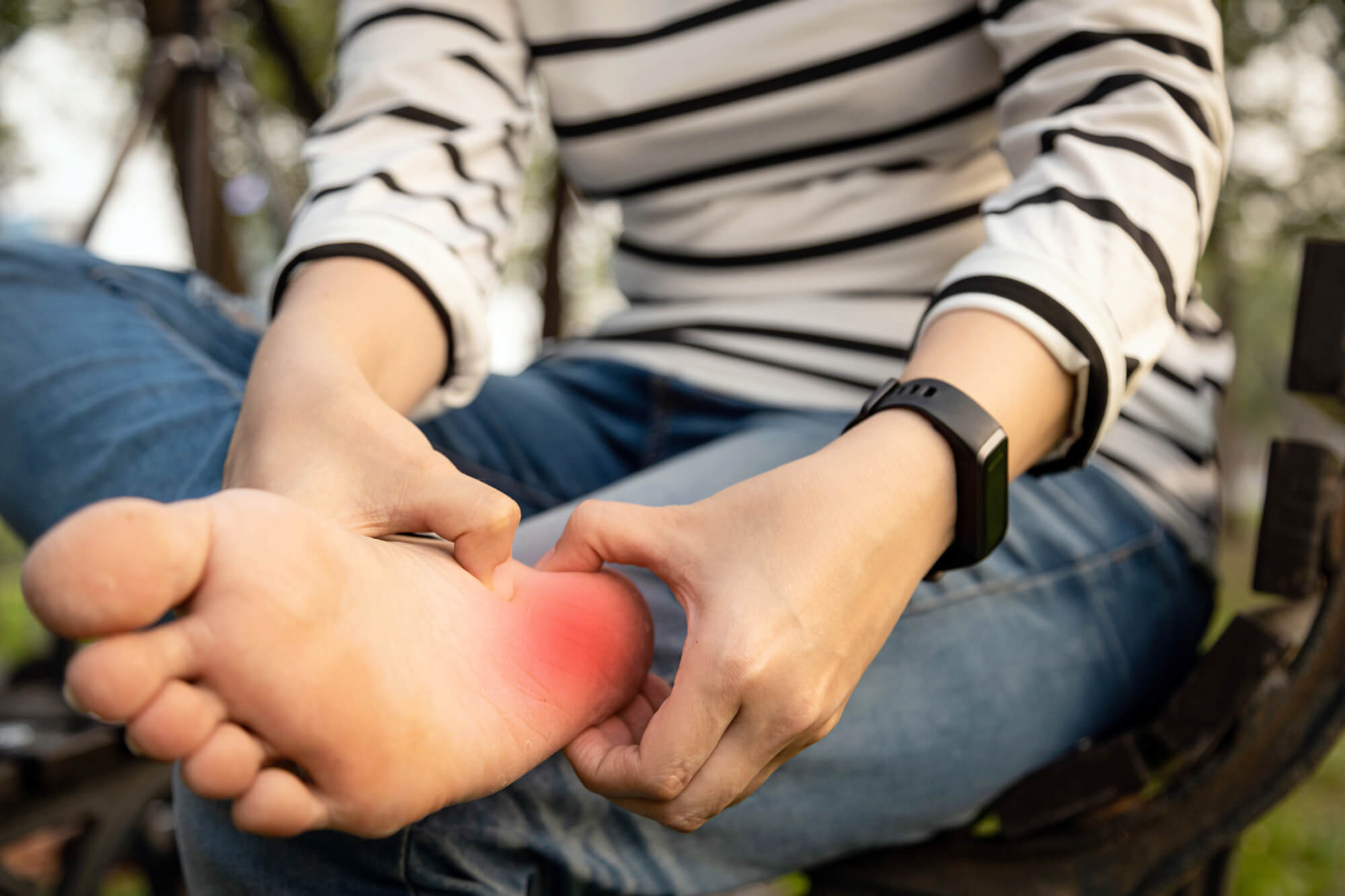

Muscle Cramps and Magnesium Deficiency
Muscle cramps are a common complaint among those with plantar fasciitis. Magnesium deficiency has been associated with an increased susceptibility to muscle cramps and spasms. Magnesium plays a key role in muscle contraction and relaxation. Insufficient magnesium levels can disrupt the delicate balance between these processes, leading to muscle imbalances, spasms, and cramping.
Pain Perception and Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency may also affect pain perception in individuals with plantar fasciitis. Studies suggest that magnesium influences pain-signaling pathways in the body. Inadequate magnesium levels can alter pain sensitivity, making individuals more prone to experiencing heightened pain sensations. This can contribute to the intensity of heel pain experienced in plantar fasciitis.
Addressing Magnesium Deficiency for Plantar Fasciitis Relief
Addressing magnesium deficiency can alleviate symptoms and promote healing in individuals with plantar fasciitis. Increasing magnesium intake through dietary sources and considering magnesium supplementation may help rebalance magnesium levels in the body.
Benefits of Magnesium for Plantar Fasciitis Relief
Alleviating Inflammation and Reducing Pain
One of the key benefits of magnesium for plantar fasciitis is its anti-inflammatory properties. Magnesium is a natural anti-inflammatory agent, helping reduce inflammation in the plantar fascia. Magnesium can alleviate pain and discomfort associated with plantar fasciitis by inhibiting the release of inflammatory mediators and modulating the immune response.
Supporting Tissue Repair and Healing
Magnesium plays a crucial role in the process of tissue repair and regeneration. Adequate magnesium levels are essential for collagen synthesis, a structural protein that forms the building blocks of tissues, including the plantar fascia. By promoting collagen production, magnesium supports the healing process of the damaged plantar fascia, aiding in tissue repair and reducing recovery time.
Preventing Muscle Cramps and Spasms
Muscle cramps and spasms are common symptoms experienced by individuals with plantar fasciitis. Magnesium is involved in muscle contraction and relaxation. It helps regulate the balance between calcium and magnesium levels within muscle cells. Insufficient magnesium can disrupt this balance, leading to muscle imbalances, spasms, and cramping. By replenishing magnesium levels, muscle cramps can be reduced, providing relief and improving overall foot comfort.
Enhancing Pain Management
Magnesium's role in pain modulation extends beyond its anti-inflammatory properties. It also influences pain perception and sensitivity. Studies have shown that magnesium can interact with pain receptors in the nervous system, reducing the transmission of pain signals and promoting pain relief. By supplementing with magnesium, individuals with plantar fasciitis may experience decreased intensity and frequency of pain associated with the condition.
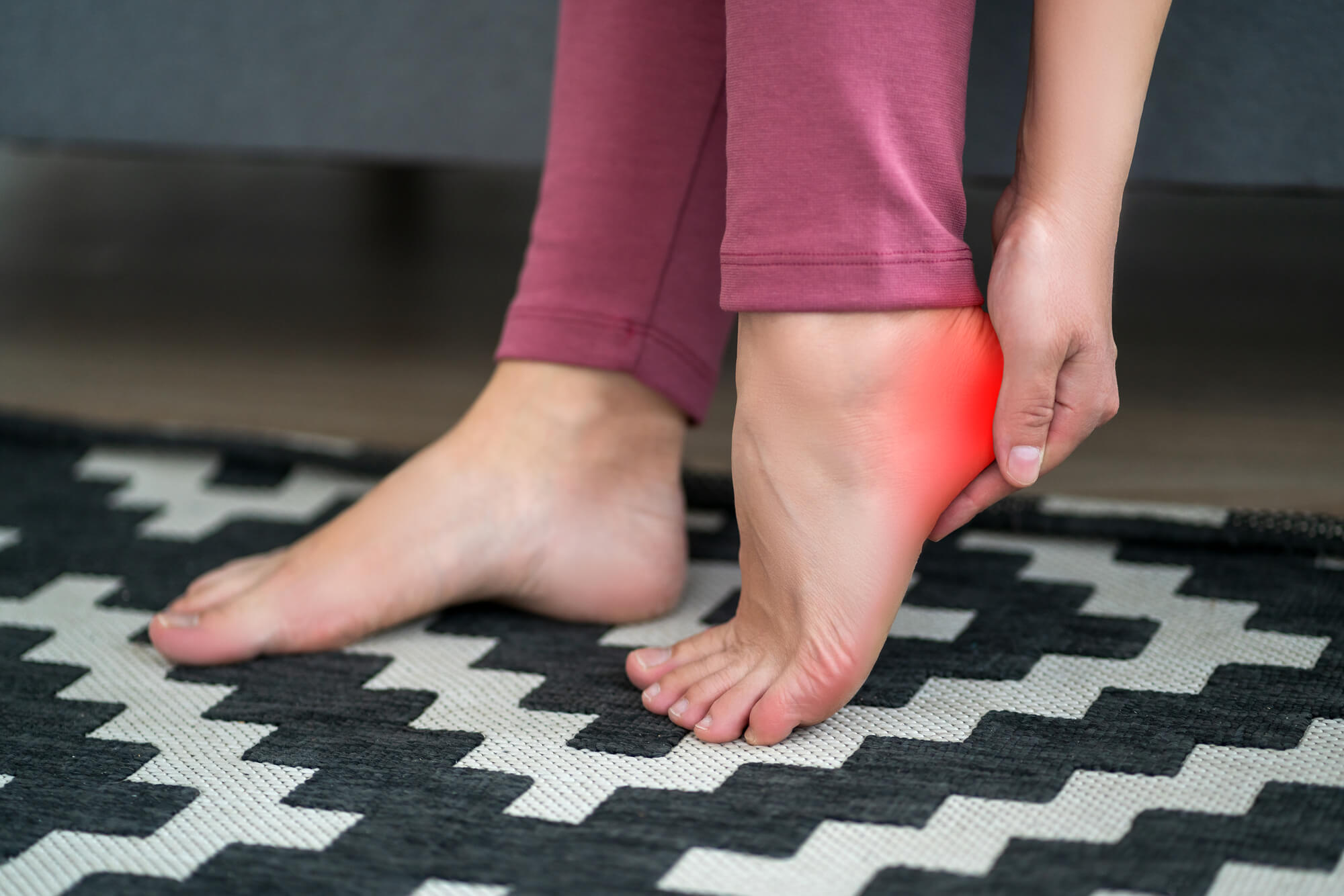
Supporting Overall Foot Health
Beyond its specific benefits for plantar fasciitis, magnesium contributes to overall foot health. It helps maintain optimal muscle function, including the muscles supporting the arch of the foot. By promoting muscle relaxation and preventing muscle imbalances, magnesium supports proper foot mechanics and reduces the risk of further foot-related issues.
Food Sources of Magnesium
Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet is an excellent way to support foot health and potentially reduce plantar fasciitis symptoms. Good food sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables (such as spinach and kale), nuts and seeds (like almonds and pumpkin seeds), legumes, whole grains, and fish.
Magnesium Supplementation Options
For individuals with plantar fasciitis, magnesium supplements can be a convenient way to ensure adequate magnesium intake. Various forms of magnesium supplements are available, including magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right type and dosage of magnesium supplement suitable for your specific needs.
Proper Dosage and Usage Guidelines
The appropriate dosage of magnesium supplementation depends on factors such as age, sex, and overall health. General recommendations suggest a daily magnesium intake of around 400-420 mg for men and 310-320 mg for women. However, individual needs may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the optimal dosage for plantar fasciitis relief.
Other Considerations for Plantar Fasciitis Management
While magnesium supplementation can be beneficial, it is important to remember that it should not replace other essential aspects of plantar fasciitis management. Combining magnesium supplementation with stretching exercises, physical therapy, and proper footwear can optimize results. Seeking professional advice from a podiatrist or healthcare professional will help develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Magnesium offers potential benefits for individuals with plantar fasciitis, relieving inflammation, reducing pain, and supporting muscle health. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet and considering magnesium supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare professional can be valuable additions to your plantar fasciitis management strategy.
Remember, while magnesium shows promise in alleviating plantar fasciitis symptoms, it is not a standalone solution. A comprehensive approach that combines various treatment modalities, including stretching exercises, physical therapy, and proper footwear, will yield the best results.
If you are experiencing plantar fasciitis pain and discomfort, consult with a podiatrist or healthcare professional to discuss the potential benefits of incorporating magnesium into your treatment plan. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your needs and help you navigate the appropriate dosage and usage guidelines.
By exploring the potential benefits of magnesium for plantar fasciitis relief, you are taking a proactive step towards finding natural and holistic solutions for your foot health. With proper management and a comprehensive approach, you can alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve your overall quality of life. Embrace the power of magnesium and embrace a healthier, pain-free future for your feet.

