Morton’s Neuroma Foot Squeeze Test
If you're experiencing persistent foot pain, specifically in the ball of your foot or between your toes, you may be dealing with Morton's neuroma. This common condition can cause discomfort and impact your daily activities. Fortunately, diagnostic techniques can help pinpoint the presence of Morton's neuroma, such as the Foot Squeeze Test. This article will explore the significance of clinical tests, particularly the Foot Squeeze Test, in diagnosing Morton's neuroma. We'll delve into the symptoms, causes, and various diagnostic methods to aid in accurate diagnosis and understanding of this condition. Join us as we unravel the key insights and treatment options to help you find relief from foot pain and regain your mobility.
Understanding Morton's Neuroma
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition affecting the foot's nerves. Learn about its causes, risk factors, common symptoms, and methods of diagnosis.
What is Morton's Neuroma?
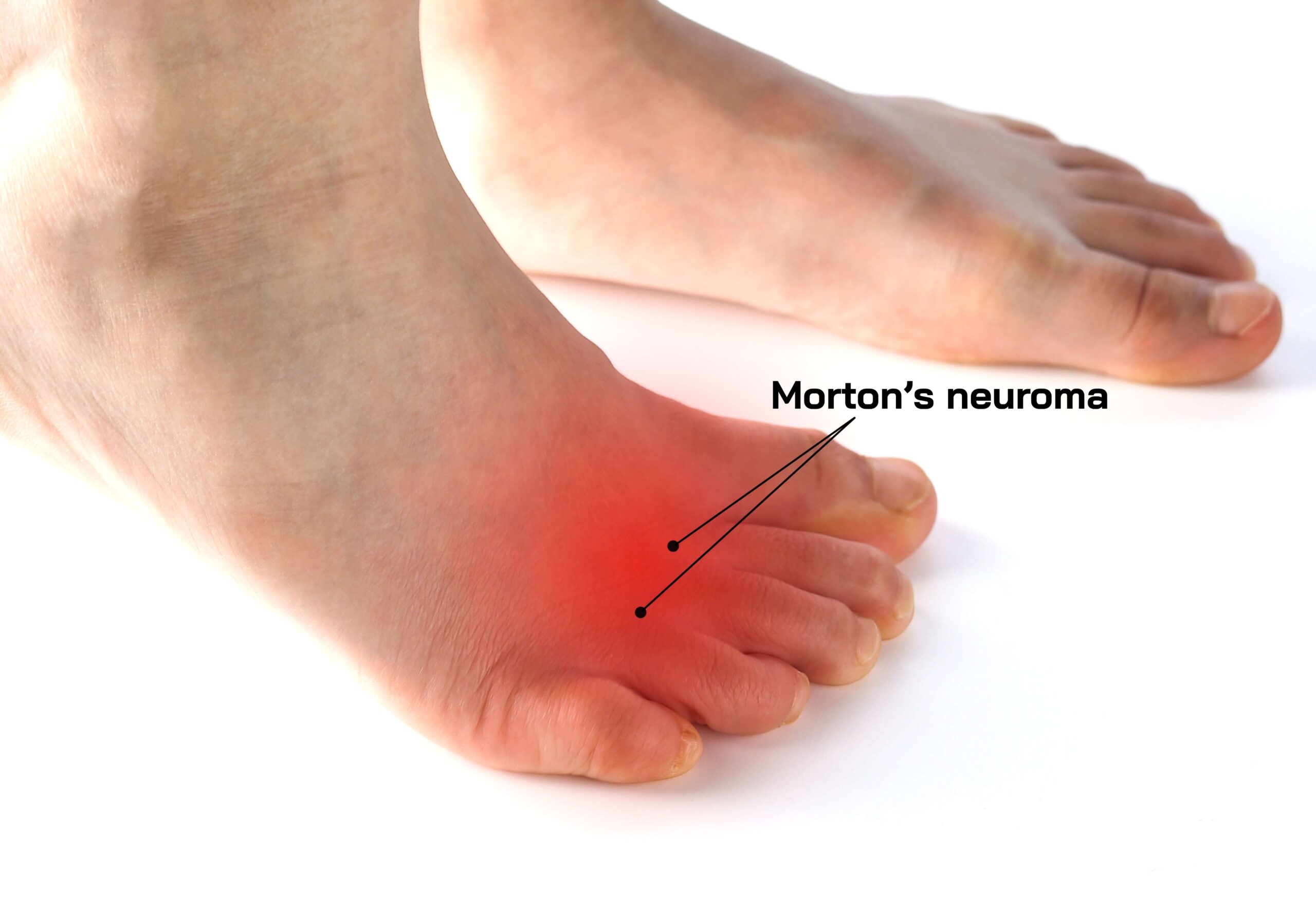
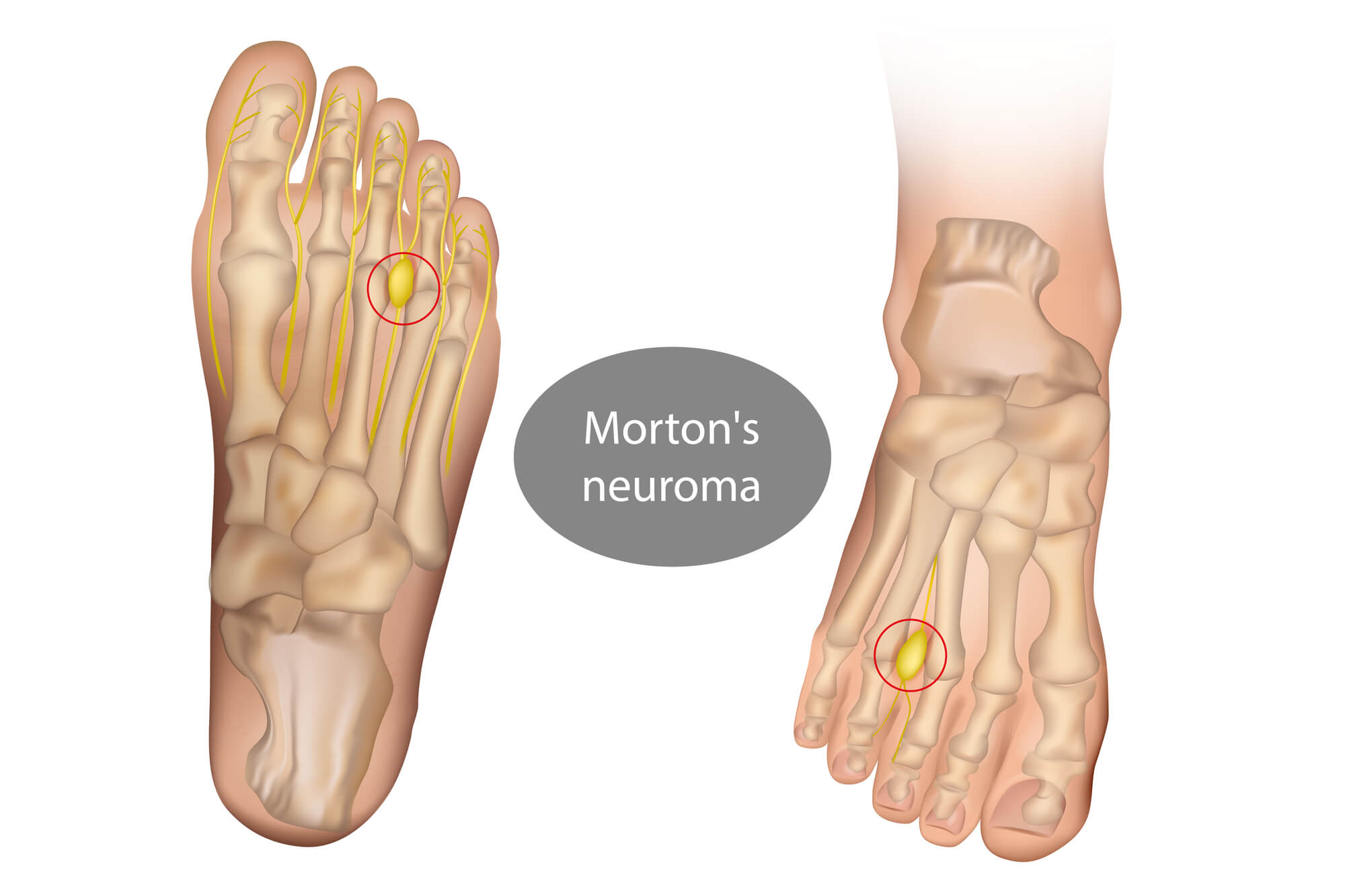
Morton's neuroma is a benign growth of tissue around the nerves that run between the metatarsal heads in the foot. It commonly affects the nerve between the third and fourth metatarsal heads.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Morton's neuroma is not fully understood. Still, certain factors, such as wearing tight shoes, high heels, or participating in high-impact activities, can increase the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Morton's neuroma can cause various symptoms, including sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot or between the toes. A thorough clinical examination is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Clinical Tests for Morton's Neuroma
Morton's neuroma can be accurately diagnosed through clinical tests and examination. These tests help assess the presence of a neuroma and its location and aid in ruling out other possible causes of foot pain.
Importance of Clinical Examination
A thorough clinical examination is crucial in evaluating foot pain and determining the likelihood of Morton's neuroma. It involves a detailed assessment of the patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination of the affected foot.
The Squeeze Test
One of the clinical tests commonly used to diagnose Morton's neuroma is the Foot Squeeze Test. This test involves applying pressure to the forefoot, specifically the metatarsal heads, to elicit a specific response indicating a neuroma.
Performing the Squeeze Test
To perform the Foot Squeeze Test, a healthcare professional applies a gentle squeeze to the forefoot, compressing the metatarsal heads together. The patient is asked to communicate any pain or discomfort experienced during the maneuver.
Interpretation and Diagnostic Value
A positive result from the Foot Squeeze Test, where the patient experiences pain or reproduction of their typical symptoms, suggests the presence of Morton's neuroma. This test helps narrow the diagnosis and provides valuable information for treatment planning. However, it is essential to consider other diagnostic factors and perform additional tests for a comprehensive evaluation.
Other Diagnostic Techniques for Morton's Neuroma
While the Foot Squeeze Test is a valuable clinical tool, other diagnostic techniques can contribute to the confirmation of Morton's neuroma and assist in ruling out other conditions causing similar symptoms.
Click Test
The Click Test is another clinical examination method used to assess the presence of Morton's neuroma. A healthcare professional applies a dorsally directed force to the metatarsal heads during this test while palpating the affected area. A palpable or audible click or snap may indicate the presence of a neuroma.
Imaging Studies for Reference
Imaging studies such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed images of the foot, visualizing the neuroma and assessing its size, location, and severity. These studies are instrumental when clinical examination alone does not provide a definitive diagnosis or when there is a need for further evaluation.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history and physical examination is essential for diagnosing Morton's neuroma accurately. The healthcare professional will ask about the patient's symptoms, duration, and aggravating factors. Additionally, they will perform a thorough physical examination to assess the affected foot, including looking for signs of inflammation, palpating the foot for tender areas, and assessing sensory changes.
Evaluation of Foot Pain and Numbness
Evaluating the distribution, characteristics, and patterns of foot pain and numbness can aid in distinguishing Morton's neuroma from other conditions affecting the foot and ankle. The healthcare professional will assess the location, intensity, and triggers of pain and any associated sensory changes to help confirm the diagnosis.
Assessing the Digital Nerve
Morton's neuroma involves irritation of the digital nerve in the foot. During the evaluation, the healthcare professional may perform specific tests to assess the function and sensitivity of the digital nerve. These tests can further support the diagnosis of Morton's neuroma and aid in ruling out other nerve-related conditions.
Treatment Options for Morton's Neuroma
Once diagnosed with Morton's neuroma, various treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and improve foot function. The treatment choice depends on the severity of the condition, the patient's preferences, and the response to conservative measures.
Conservative Management Approaches
Conservative management approaches are usually the first line of treatment for Morton's neuroma. These methods aim to relieve pressure on the affected nerve, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. They may include:
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing shoes with a wider toe box, low heels, and good arch support can help reduce forefoot compression and relieve compression.
- Padding and Orthotics: Metatarsal pads or arch supports can help offload pressure from the affected area and improve foot alignment.
- Foot Massage and Stretching Exercises: Gentle massage techniques and specific stretching exercises can help relax the foot muscles, improve blood circulation, and reduce pain.
Steroid Injection Therapy
A healthcare professional may recommend corticosteroid injections if conservative measures fail to provide sufficient relief. These injections help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain temporarily. However, it's important to note that repeated injections should be done cautiously to avoid potential complications.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention may be considered when conservative treatments are ineffective, or the condition is severe. Surgery aims to remove the neuroma or release the compressed nerve, relieving symptoms and restoring foot function. The specific surgical approach depends on the individual case and may involve minimal incisions or more extensive procedures.
Conclusion
The Morton's Neuroma Foot Squeeze Test is a valuable clinical tool for diagnosing this painful foot condition. However, it is important to consider other diagnostic techniques and conduct a comprehensive examination to accurately confirm the presence of Morton's neuroma. By implementing appropriate treatment options based on the diagnosis, individuals with Morton's neuroma can find relief from foot pain, numbness, and discomfort, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- The Morton's Neuroma Foot Squeeze Test is a valuable clinical tool for diagnosing Morton's neuroma and identifying the presence and location of the neuroma.
- Clinical examination and other diagnostic techniques, such as imaging studies and medical history evaluation, contribute to a comprehensive understanding of Morton's neuroma.
- Treatment options for Morton's neuroma range from conservative measures to surgical intervention, depending on the severity and response to non-surgical approaches.

