Shin Splints: What They Are and How to Treat Them
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are common injuries among runners and athletes participating in high-impact sports. They occur when the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg become overworked, leading to pain and inflammation along the shin bone. If left untreated, shin splints can progress to stress fractures or other more serious injuries. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options for shin splints and ways to prevent them.
What Are Shin Splints?
Definition
Shin splints refer to the pain and discomfort that occur along the shin bone, or tibia, as a result of overuse or improper technique during physical activity. The term "shin splints" is often used to describe several different types of lower leg injuries, including medial tibial stress syndrome, periostitis, and compartment syndrome.
Causes
Shin splints are typically caused by overuse or improper form during physical activity, such as running or jumping. They can also be caused by wearing improper or poorly fitting footwear or by having flat feet or high arches. Other factors that may contribute to the development of shin splints include running on uneven or hard surfaces, sudden increases in training intensity or duration, and muscle imbalances.

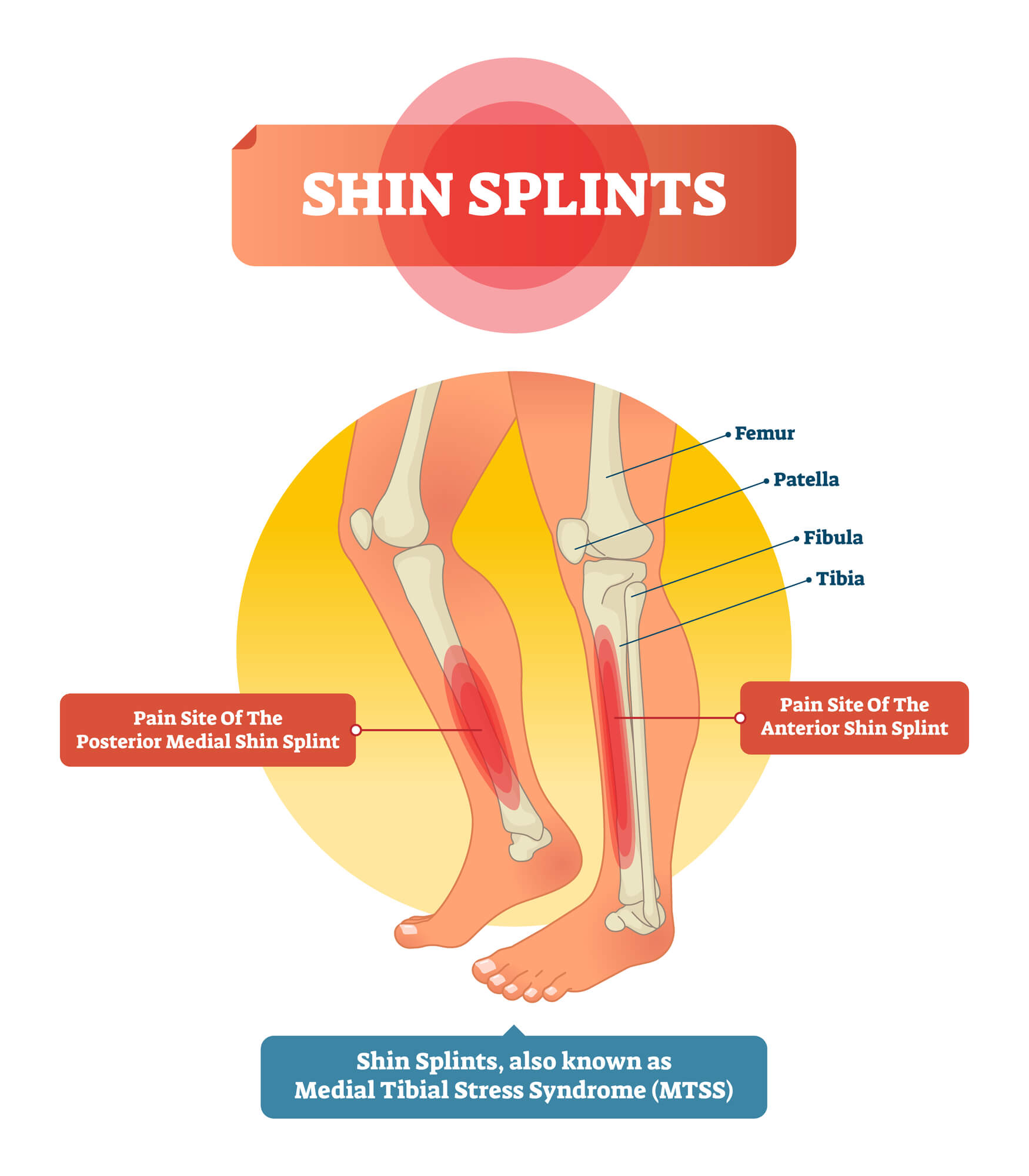
Symptoms of Shin Splints
- Pain along the shin bone: The most common symptom of shin splints is pain along the shin bone, typically on the inside part of the lower leg. This pain may be dull and aching, or it may be sharp and stabbing. It is usually most pronounced during or after physical activity and may be relieved by rest.
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected area: In addition to pain, people with shin splints may also experience swelling or tenderness in the affected area. The skin over the shin bone may feel warm to the touch and be sensitive to pressure.
How to Treat Shin Splints
Rest and Ice
The most important treatment for shin splints is rest. It is important to take a break from the activity causing the pain and allow the lower leg to heal. Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can also help to reduce swelling and pain.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching and strengthening the muscles in the lower leg can help to prevent shin splints and speed up recovery. Some exercises that may be helpful include calf stretches, toe raises, and leg presses. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist before starting any new exercise routine.
Wearing Proper Footwear
Proper footwear that fits well and provides adequate support is crucial for preventing and treating shin splints. Running shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help to absorb the shock of impact and reduce the risk of shin splints. If you have flat feet or high arches, you may benefit from using orthotics, which can be placed in your shoes to provide additional support.
Seeking Medical Attention if Necessary
In some cases, shin splints may be caused by a more serious underlying condition, such as a stress fracture or tendonitis. If you experience severe pain, swelling, or difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare provider or podiatrist can perform a physical exam and possibly order an x-ray or other imaging tests to diagnose the cause of the pain.
Preventing Shin Splints
Gradually Increasing Intensity and Duration of Physical Activity
Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of your physical activity can help to prevent shin splints. If you are new to running or are returning to an activity after a long break, it is important to start slowly and gradually build up your endurance. Increasing your training too quickly can strain the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg and increase your risk of shin splints.
Wearing Proper Footwear
As mentioned earlier, wearing proper footwear that fits well and provides adequate support is crucial for preventing shin splints. Choose running shoes with good arch support and cushioning, and replace them every 300-500 miles or when they show signs of wear. If you have flat feet or high arches, consider using orthotics or custom-made inserts to provide additional support.
Stretching Before and After Exercise
Stretching before and after exercise can help to prevent shin splints by improving flexibility and reducing muscle imbalances. Some stretches that may be helpful include calf stretches, toe raises, and leg presses. Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds and repeat on both sides.
Varying Your Workouts to Avoid Overuse Injuries
Varying your workouts can help to prevent overuse injuries like shin splints. If you typically run, try incorporating other low-impact activities like swimming or cycling into your routine. This can give your lower legs a break and reduce the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Shin splints are common injuries caused by overuse or improper form during physical activity. Symptoms include pain along the shin bone, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. Rest, ice, stretching and strengthening exercises, and wearing proper footwear can all help to treat and prevent shin splints. If you experience severe pain or swelling, it is important to seek medical attention to rule out more serious underlying conditions. You can continue to stay active and healthy with proper prevention and treatment.
FAQ
What is the fastest way to relieve shin splints?
The fastest way to relieve shin splints is to rest and ice the affected area. This can help to reduce pain and swelling. Stretching and strengthening exercises may also help relieve symptoms and promote healing. If the pain is severe or does not improve with self-care measures, it is important to seek medical attention.
What are shin splints and how are they treated?
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are common injuries among runners and athletes participating in high-impact sports. They occur when the muscles, tendons, and bone tissue in the lower leg become overworked, leading to pain and inflammation along the shin bone. To treat shin splints, it is important to rest and ice the affected area and to stretch and strengthen the muscles in the lower leg. Wearing proper footwear and gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activity can also help to prevent and treat shin splints.
How long do shin splints take to fully heal?
The length of time it takes for shin splints to heal fully can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment being used. In general, giving the lower leg sufficient time to rest and heal before returning to physical activity is important. Depending on the individual case, this can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
What is the most common cause of shin splints?
The most common cause of shin splints is overuse or improper form during physical activity, such as running or jumping. They can also be caused by wearing improper or poorly fitting footwear or having flat feet or high arches. Other factors that may contribute to the development of shin splints include running on uneven or hard surfaces, sudden increases in training intensity or duration, and muscle imbalances.

