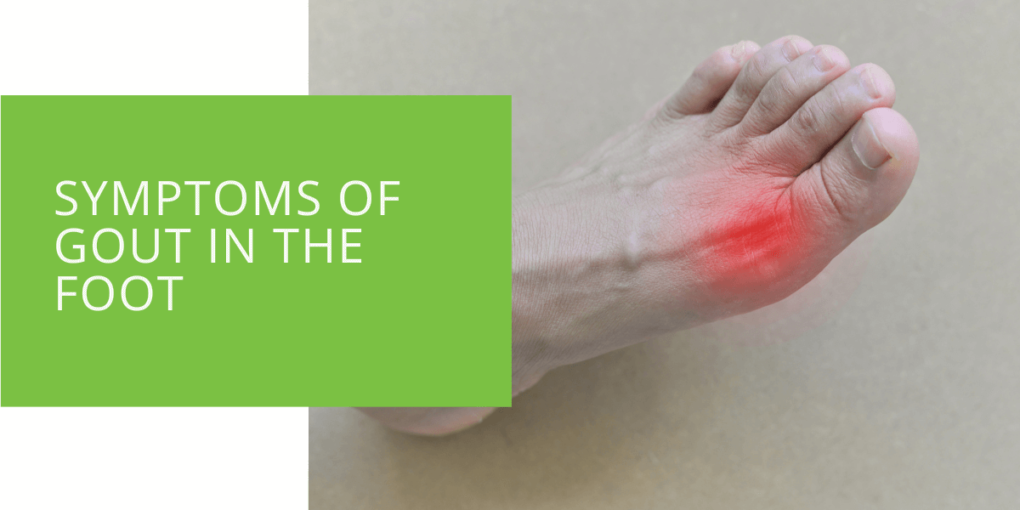
Symptoms of Gout in the Foot
Gout is a form of arthritis that affects the joints, particularly in the foot. It is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can form crystal deposits in the joints and cause inflammation and pain. Gout symptoms can be severe and include intense pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of gout in the foot, the causes and risk factors for gout, and the available treatment options. We will also discuss strategies for preventing gout flare-ups and managing this form of arthritis effectively. If you or a loved one is experiencing gout symptoms, it is important to seek prompt medical treatment to prevent long-term complications.
What Is Gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by high uric acid levels in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product produced when the body breaks down purines, found in certain foods such as red meat and seafood. In people with gout, the body either produces too much uric acid or cannot remove it effectively from the bloodstream. As a result, uric acid crystals can form in the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Gout is more common in men than in women, and the risk of developing gout increases with age. Other factors that can increase the risk of gout include a family history of the condition, certain medical conditions (such as high blood pressure or kidney disease), and certain medications (such as diuretics or aspirin).
Symptoms of Gout in The Foot
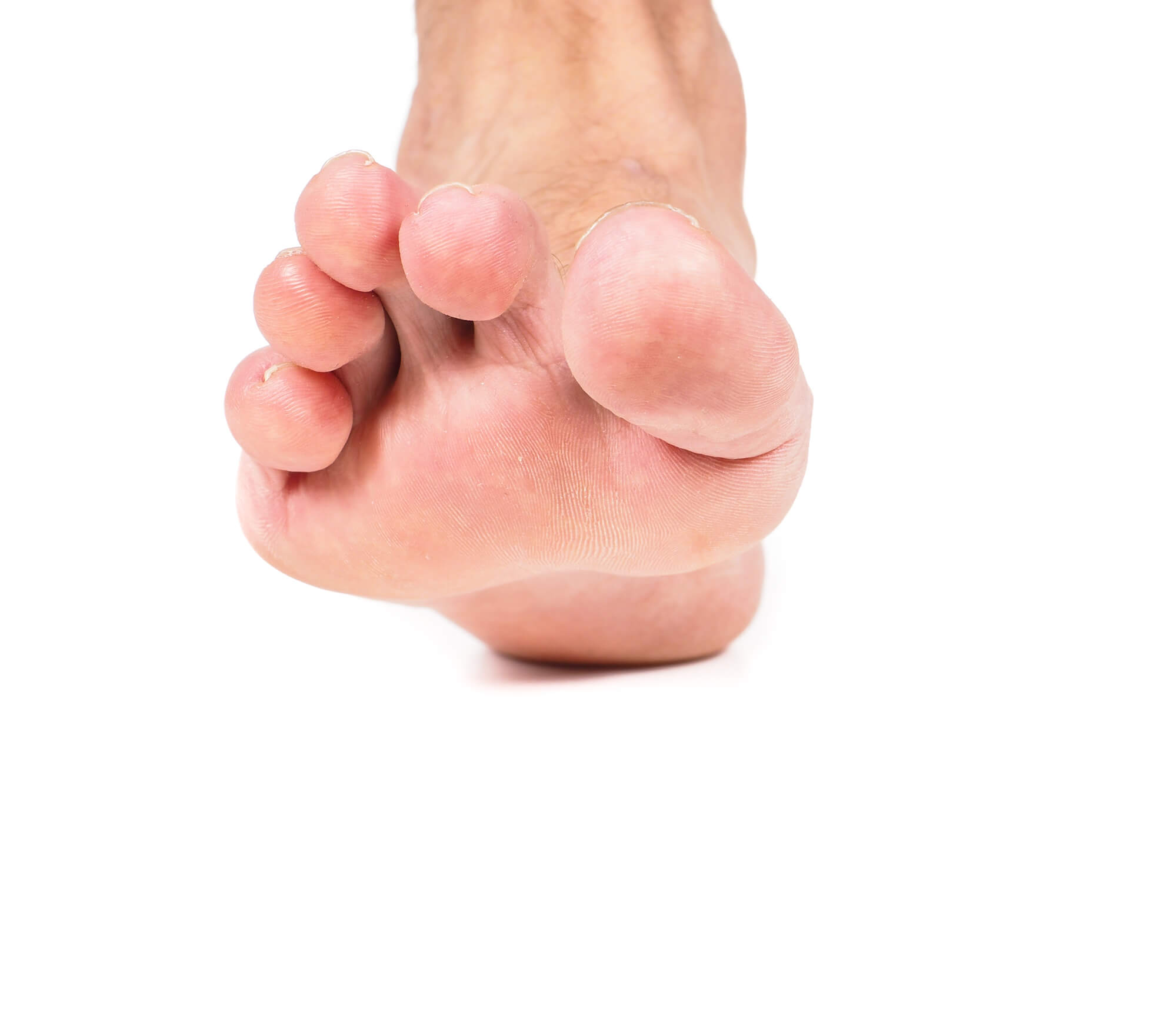
Gout most commonly affects the big toe, but it can also affect other joints in the foot, such as the ankle or heel. The most common foot gout symptom is intense pain in the affected joint. The pain is usually sudden and severe and may be accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected area. The joint may also feel tender or sensitive to touch, and it may be difficult to walk or bear weight on the affected foot.
During a gout attack, the affected joint may also have a limited range of motion. Small lumps called tophi may sometimes form under the skin near the affected joint. Tophi are made up of accumulated uric acid crystals in the tissue.

Diagnosis and Treatment of Gout
If you suspect gout, it is important to see a podiatrist or other healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. A podiatrist will ask about your symptoms and medical history and may also order lab tests to measure uric acid level in your blood. Imaging studies, such as an X-ray or MRI, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis of gout.
Treatment for gout involves managing the pain and reducing the levels of uric acid in the blood. This may include medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine, which can help reduce inflammation and pain. In some cases, medications that lower uric acid levels in the blood may be prescribed.
Lifestyle changes, such as following a healthy diet and exercising regularly, can also help reduce the risk of gout flare-ups. Avoiding foods high in purines, such as red meat and seafood, can help lower uric acid levels in the blood. It is also important to stay hydrated and maintain a healthy weight, as these factors can help reduce gout risk.
Preventing Gout Flare-Ups
Several strategies can help prevent gout attacks and reduce the risk of flare-ups. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle: As mentioned above, following a healthy diet low in purines and staying hydrated can help lower uric acid levels in the blood and prevent gout attacks. Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of gout.
- Managing medical conditions: If you have certain medical conditions, such as high blood pressure or kidney disease, it is important to follow your treatment plan and manage these conditions effectively. This can help prevent gout attacks and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
- Avoiding triggers: Some people with gout may have specific triggers that can increase the risk of a flare-up. These may include certain foods, alcohol, or medications. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, you can help reduce the risk of gout attacks.
- Seeking prompt treatment: If you have symptoms of gout, it is important to see a podiatrist or other healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early treatment can help prevent long-term complications and reduce the severity of gout attacks.
Takeaways
Gout is a form of arthritis that can cause pain and swelling in the joints, particularly in the foot. It is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can form crystals in the joints and cause inflammation. Symptoms of gout in the foot include intense pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area. Gout can be effectively managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. Understanding the symptoms and seeking prompt treatment can help prevent long-term complications from gout.
Conclusion
Gout is a common form of arthritis that can cause intense pain and swelling in the joints, particularly in the foot. If you have signs and symptoms of gout, it is important to see a podiatrist or other healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment. By managing gout and reducing the risk of flare-ups, you can help prevent long-term complications and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of gout in the foot?
The most common symptom of gout in the foot is intense pain in the affected joint, typically the big toe. Other symptoms may include swelling and redness in the affected area, tenderness or sensitivity to touch, difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected foot, and limited range of motion in the affected joint. In some cases, small lumps called tophi may form under the skin near the affected joint.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product produced when the body breaks down purines, found in certain foods such as red meat and seafood. In people with gout, the body either produces too much uric acid or cannot remove it effectively from the bloodstream. As a result, uric acid crystals can form in the joints, causing inflammation and pain.
Can gout cause severe pain?
Yes, gout can cause severe pain. The pain is usually sudden and severe and may be accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected area. The joint may also feel tender or sensitive to touch, and it may be difficult to walk or bear weight on the affected foot.
What is an attack of gout?
An attack of gout, also known as a flare-up or episode, is a period of time when the symptoms of gout are particularly severe. Gout attacks can last for several days or longer, and they may be triggered by certain factors, such as certain foods or medications.
How often does gout usually occur?
The frequency of gout attacks can vary greatly from person to person. Some people may only have one or two attacks in their lifetime, while others may experience frequent flare-ups. The severity and frequency of gout attacks can be influenced by various factors, such as the level of uric acid in the blood, other medical conditions, and lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise.