How Podiatrists Use Ultrasound to Diagnose Foot and Ankle Conditions
Ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool podiatrists use to diagnose and treat foot and ankle conditions. It is a non-invasive, painless technique that uses sound waves to produce images of internal structures, allowing podiatrists to identify various conditions. In this article, we'll explore how podiatrists use ultrasound to diagnose foot and ankle conditions, its benefits, and how it compares to other diagnostic methods.
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal organs and tissues. In podiatry, it examines the foot and ankle and identifies various conditions affecting these areas. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, ultrasound does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative for patients.
What Conditions Can Be Diagnosed with Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is an effective tool for diagnosing various foot and ankle conditions. Some of the conditions that can be diagnosed using ultrasound include:
- Plantar fasciitis: inflammation of the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot
- Tendinitis: inflammation of a tendon, often the Achilles tendon or the posterior tibial tendon
- Neuromas: benign growth of nerve tissue that can cause pain and discomfort
- Sprains: stretching or tearing of a ligament in the foot or ankle
- Bursitis: inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints
- Stress fractures: tiny cracks in the bone caused by overuse or repetitive stress
- Arthritis: inflammation of a joint, often caused by wear and tear or an autoimmune disorder
Ultrasound can also examine the soft tissues of the foot and ankle, such as muscles and ligaments.
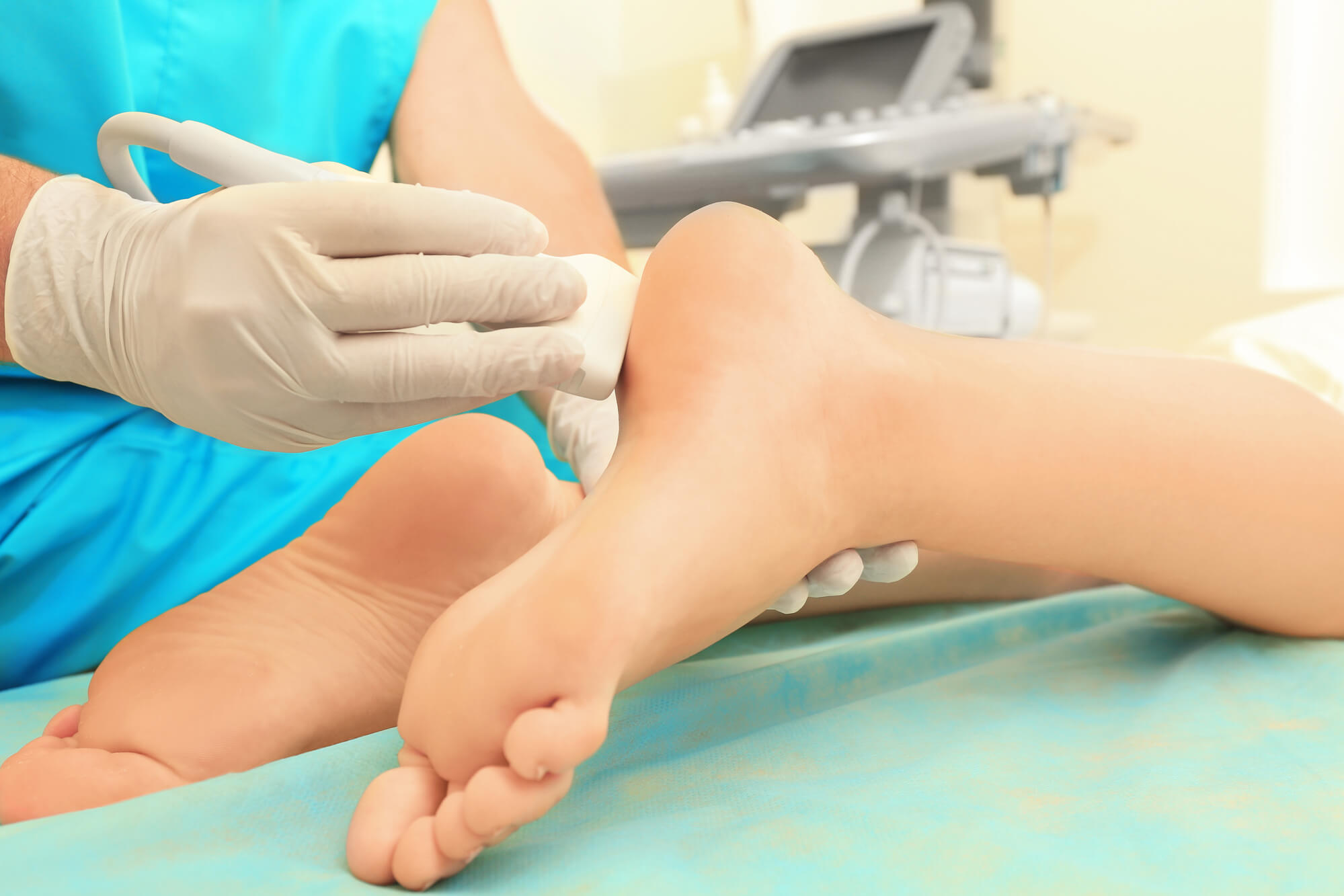
The Ultrasound Process in Podiatry
When a patient comes in with foot or ankle pain, a podiatrist may order an ultrasound to help diagnose the condition. During the exam, the patient lies on an exam table, and a gel is applied to the skin to help the sound waves travel more easily. The podiatrist then uses a handheld transducer to send sound waves through the skin and into the foot or ankle. The sound waves bounce off internal structures and create images that the podiatrist can use to diagnose the condition.
The ultrasound process is painless and usually takes 15-30 minutes. It does not involve needles or incisions, making it a safer and less invasive alternative to other diagnostic methods.
Benefits of Ultrasound in Podiatry
There are many benefits of using ultrasound in podiatry. For one, it is a non-invasive, painless technique that does not involve ionizing radiation. This makes it a safer alternative to X-rays and CT scans, particularly for pregnant women and children.
Ultrasound is also highly accurate, allowing podiatrists to see the internal structures of the foot and ankle in real time. This makes diagnosing conditions easier and creating a treatment plan tailored to the patient's needs.
Finally, ultrasound is a versatile technique that can diagnose various foot and ankle conditions, from sprains and strains to neuromas and stress fractures. It can also be used to examine the soft tissues of the foot and ankle, such as muscles and ligaments.

How Ultrasound Compares to Other Diagnostic Methods
While ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool, it is not always the best choice for every patient. In some cases, X-rays or MRI scans may be more appropriate, depending on the diagnosed condition. For example, X-rays often diagnose fractures or bone abnormalities, while MRI scans are useful for examining soft tissue structures, such as tendons and ligaments.
However, ultrasound is often the preferred choice for diagnosing foot and ankle conditions. It is a faster and more cost-effective method than MRI, providing real-time images and making it easier for podiatrists to identify conditions that may not be visible on X-rays.
Using Ultrasound for Treatment
In addition to diagnosing foot and ankle conditions, podiatrists can also use ultrasound to treat them. One technique is called ultrasound-guided injection, where medication, such as cortisone, is injected directly into the affected area. This method is often used to treat plantar fasciitis or Achilles tendinitis.
Another technique is therapeutic ultrasound, where sound waves promote healing and reduce pain and inflammation. This is achieved by increasing blood flow to the affected area, promoting healing, and reducing inflammation.
Conclusion
Ultrasound is a valuable tool that podiatrists use to diagnose and treat foot and ankle conditions. It is a non-invasive, painless technique that provides real-time images of internal structures, making diagnosing conditions easier and creating a treatment plan tailored to the patient's needs. While it is not always the best choice for every patient, it is often the preferred diagnostic method for foot and ankle conditions. If you are experiencing foot or ankle pain, contact a podiatrist to learn more about how ultrasound can help you.
In summary, ultrasound is an effective and safe method of diagnosing and treating foot and ankle conditions. It provides clear images of internal structures, allowing podiatrists to diagnose various conditions, from plantar fasciitis to stress fractures. It is also non-invasive and painless, making it a safer alternative to other diagnostic methods. Using ultrasound, podiatrists can provide patients with an accurate diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.