Ice or Heat for Shin Splints: Which is Better?
Shin splints are a common injury that affects many runners and athletes. The pain and discomfort can be debilitating, making it difficult to walk or run. Fortunately, there are several treatments available, including ice and heat therapy. This article will explore the benefits of ice and heat treatment for shin splints, when to use them, and how to prevent them from occurring.
What are Shin Splints?
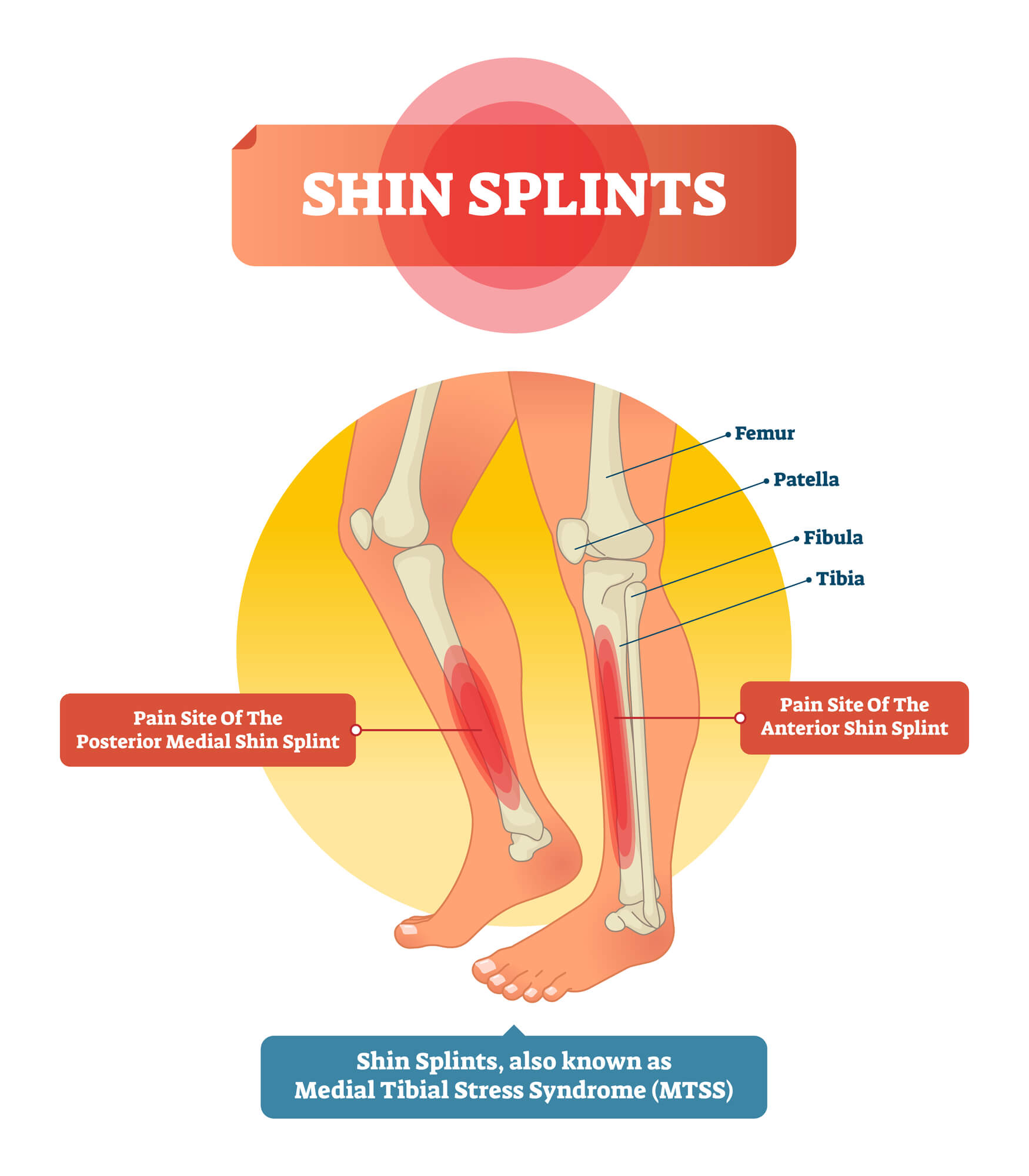
Shin splints, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, are a common condition that causes pain and inflammation along the shin bone (tibia). The pain is usually felt in the lower leg and can be caused by overuse, running on hard surfaces, or training too hard too quickly. The condition is common among runners and athletes but can also affect individuals who participate in activities that stress the lower leg muscles.
Symptoms of Shin Splints
- Pain and tenderness along the shin bone
- Swelling in the lower leg
- Inflammation
- Dull or sharp pain in the shin
- Pain that is worse during or after exercise
- Pain that may go away with rest but returns when the activity is resumed
Ice or Heat: Which is Best for Shin Splints
Both ice and heat therapy are effective treatments for shin splints, but the choice between the two depends on the stage of the injury and personal preference.
Ice Therapy
Ice therapy, also known as cryotherapy, involves applying a cold compress to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Ice therapy is particularly effective for shin splints because it constricts blood vessels, which reduces swelling and numbs the affected area. To apply ice therapy, fill a plastic bag with ice cubes or use an ice pack, wrap it in a towel, and apply it to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, for the first few days after the onset of symptoms.
Benefits of Ice Therapy for Shin Splints
- Reduces inflammation and swelling
- Numbs the affected area, reducing pain
- Improves circulation to the area
Heat Therapy
Heat therapy, also known as thermotherapy, involves applying heat to the affected area to increase blood flow and relax muscles. Heat therapy is particularly effective for shin splints because it helps increase blood flow to the affected area, speeding up the healing process. To apply heat therapy, use a heating pad or a hot towel on the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, after the initial inflammation has subsided.
Benefits of Heat Therapy for Shin Splints
- Increases blood flow to the affected area
- Relaxes muscles and reduces stiffness
- Provides pain relief
When to Use Ice or Heat for Shin Splints
The choice between ice or heat therapy depends on the stage of the injury and personal preference. Ice therapy is generally best for the first few days after the onset of symptoms when inflammation and pain are at their peak. Heat therapy is best after the initial inflammation has subsided and the muscles are sore and stiff. It is important to note that some individuals may find that one therapy is more effective than the other.
Preventing Shin Splints
To prevent shin splints, it is important to wear proper footwear, stretch before and after exercise, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Listening to your body and resting when you feel pain or discomfort is also essential.
When to See a Podiatrist for Shin Splints
If self-treatment is ineffective and symptoms persist or worsen, it is essential to seek medical advice from a podiatrist. A podiatrist can diagnose the severity of the injury and recommend the appropriate treatment. Treatment may include physical therapy, orthotics, or in severe cases, surgery. Untreated shin splints can lead to more serious conditions, such as a stress fracture or compartment syndrome, which can be more difficult to treat.
In addition to seeking medical advice, there are several other ways to eliminate shin splints. Rest and ice therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation. Compression wraps can also help reduce swelling and support the leg muscles. Over-the-counter pain medication such as ibuprofen can also help manage pain and inflammation. It is important to note that these treatments are not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Preventing Shin Splints
Preventing shin splints is key to avoiding the pain and discomfort associated with this condition. Here are some tips to help you prevent shin splints:
- Wear proper footwear: Wearing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support can help prevent shin splints. Look for shoes that have good arch support and cushioning.
- Stretch before and after exercise: Stretching can help warm the muscles and prevent injury. Make sure to stretch your calf muscles, as tight calf muscles can contribute to shin splints.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts: Increasing your workout intensity or duration too quickly can stress the lower leg muscles, leading to shin splints. Gradually increase your workout intensity or duration to avoid injury.
- Listen to your body: If you feel pain or discomfort in your lower leg, stop exercising and rest. Exercising with pain can worsen the injury and make it harder to treat.
Conclusion
Shin splints can be a painful and frustrating condition, but proper treatment and prevention can manage the symptoms and get back to pain-free activity. Ice and heat therapy are both effective treatments for shin splints, but it is important to choose the right therapy for the stage of the injury and personal preference. By taking preventive measures, listening to your body, and seeking prompt medical advice when necessary, you can manage your shin splints and continue to enjoy your daily activities without pain or discomfort.

