Plantar Fasciitis in Both Feet
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that affects the plantar fascia, a band of tissue that runs along the bottom of your foot from the heel bone to the arch. This condition can cause pain and inflammation, especially in the heel area. This article will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for plantar fasciitis, including the use of orthotics and other recommended therapies to help manage this condition.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis in Both Feet
A variety of factors can cause plantar fasciitis in both feet. Understanding these causes can help you take steps to prevent the development or worsening of this condition.
Overuse
Overuse is one of the most common causes of plantar fasciitis in both feet. Individuals who engage in high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, or who spend long periods standing or walking on hard surfaces may be at increased risk of developing this condition. Repetitive motions can lead to tiny tears in the plantar fascia, which can cause inflammation and pain.
Footwear
Wearing shoes with poor arch support, inadequate cushioning, or improper fit can also contribute to developing plantar fasciitis in both feet. Shoes worn out or too tight can increase the pressure on the plantar fascia, leading to inflammation and pain.
Flat Feet or High Arches
Flat feet or high arches can also be a risk factor for plantar fasciitis in both feet. Flat feet can cause the plantar fascia to stretch excessively, while high arches can increase stress on the heel and ball of the foot.
Tight Calf Muscles and Achilles Tendons
Tight calf muscles and Achilles tendons can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis in both feet. When these muscles are tight, they can pull on the plantar fascia, increasing the risk of inflammation and pain.
Aging
As we age, the plantar fascia can become weaker and more susceptible to injury. This can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis in both feet, especially in individuals who are overweight or have a history of foot or ankle injuries.
Genetics
Some individuals may be more genetically predisposed to developing plantar fasciitis in both feet. If you have a family history of this condition, you may be at increased risk of developing it yourself.
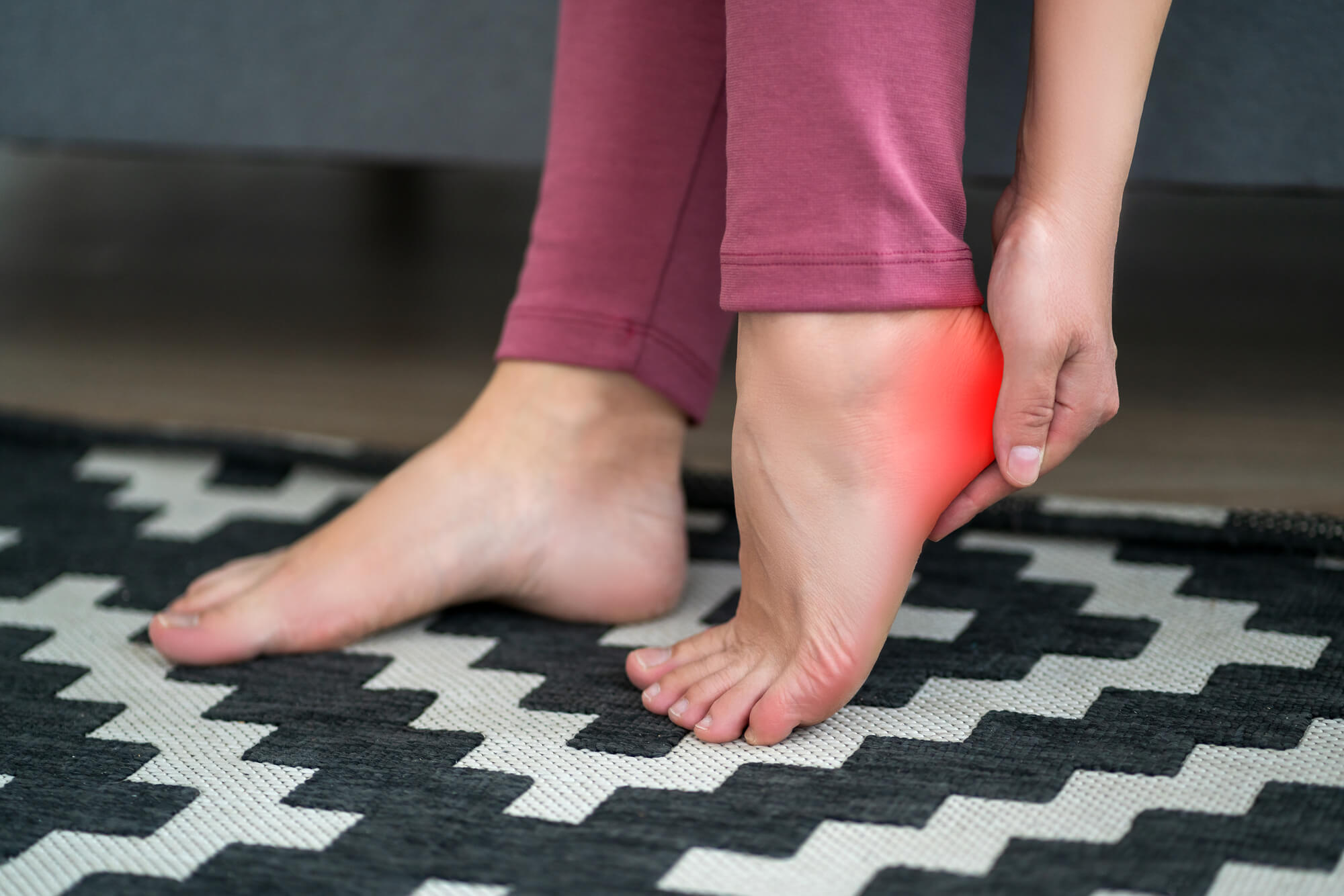
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis in Both Feet
Plantar fasciitis in both feet can cause various symptoms, varying in severity. Understanding these symptoms can help you identify this condition and seek appropriate treatment.
Heel Pain
Heel pain is the most common symptom of plantar fasciitis in both feet. The pain is typically located on the bottom of the heel and can be described as a sharp, stabbing. The pain may worsen in the morning or after long rest periods, such as sitting or sleeping. It may also be worse after prolonged periods of standing or walking.
Arch Pain
Some individuals with plantar fasciitis in both feet may also experience pain in the arch of the foot. This pain is typically felt in the middle of the foot and can be described as a dull ache or soreness.
Tenderness
The affected area may also be tender to the touch. Pressing on the bottom of the heel or the arch of the foot can cause discomfort and pain.
Stiffness
Individuals with plantar fasciitis in both feet may also experience stiffness or a limited range of motion in the foot and ankle. This can make standing, walking, or engaging in physical activities difficult.
Inflammation
Plantar fasciitis in both feet can also cause inflammation in the affected area. This can result in redness, swelling, and warmth around the heel and arch of the foot.
Heel Spur
In some cases, plantar fasciitis in both feet can lead to the development of a heel spur, which is a bony growth that forms on the heel bone. Heel spurs can cause additional pain and discomfort in the affected area.
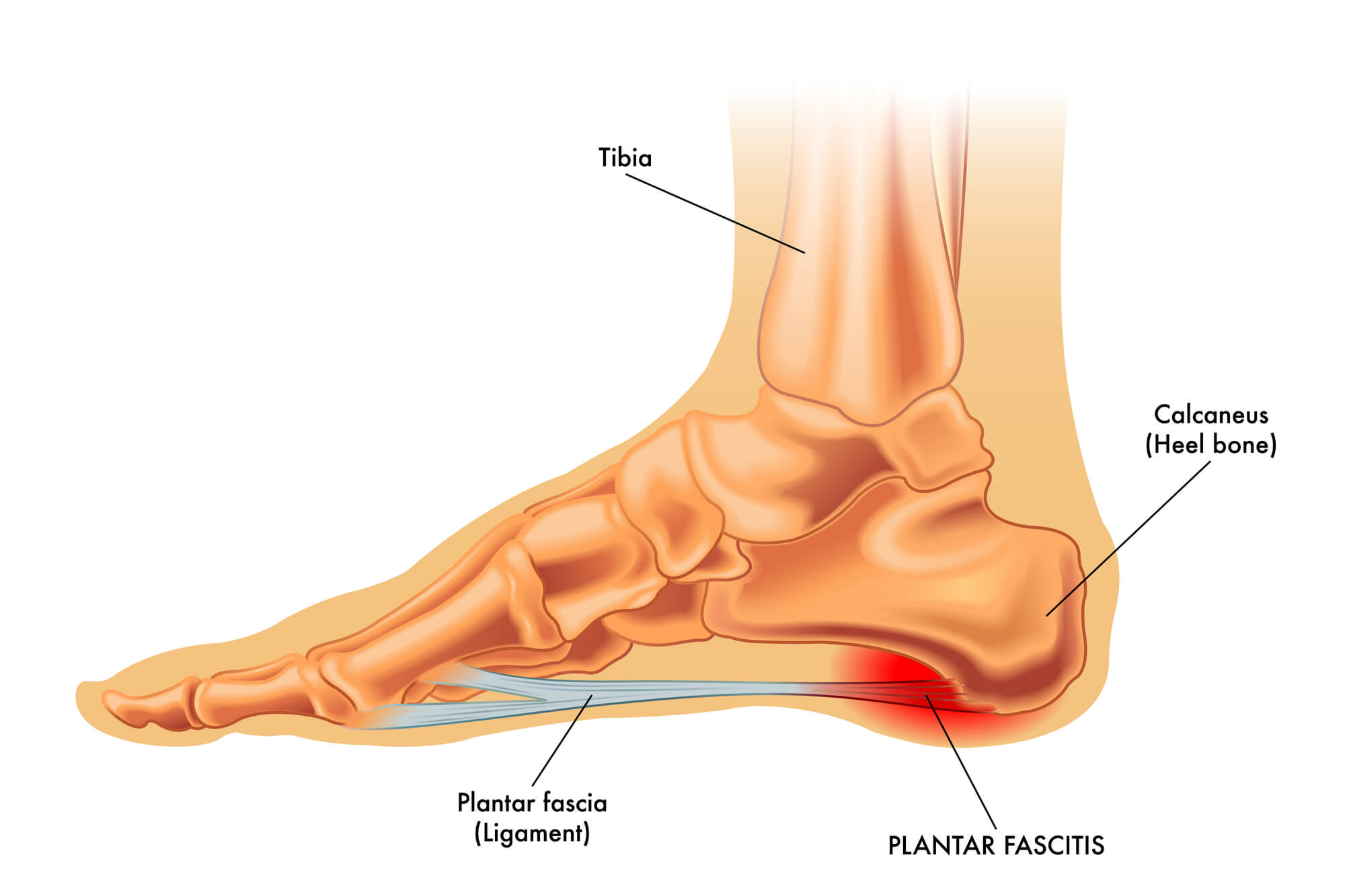
Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis
Physical Examination
A physical examination is the first step in diagnosing plantar fasciitis in both feet. The healthcare professional will evaluate your feet during this exam and ask about your symptoms. They may also perform various tests, such as applying pressure to the bottom of your feet to check for tenderness or swelling.
Medical History
Your medical history can also be important in diagnosing plantar fasciitis in both feet. The healthcare professional may ask you about any previous foot injuries or medical conditions, as well as your occupation and physical activity level.
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging, such as an X-ray or ultrasound, may also be used to diagnose plantar fasciitis in both feet. These tests can help identify any abnormalities or injuries in the feet contributing to your symptoms.
Assessment of Arch and Achilles Tendon
The healthcare professional may also assess the arch of your feet and the strength and flexibility of your Achilles tendon. Flat feet or high arches, as well as tight calf muscles and Achilles tendons, can be risk factors for plantar fasciitis in both feet. Understanding these factors can help the healthcare professional develop an appropriate treatment plan.

Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis in Both Feet
Plantar fasciitis in both feet can be a painful and debilitating condition. However, there are several treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Rest and Ice
Resting and icing the affected area is one of the first steps in treating plantar fasciitis in both feet. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. It is recommended to avoid high-impact activities and to rest the feet as much as possible.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can also help manage pain and inflammation associated with plantar fasciitis in both feet.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for plantar fasciitis in both feet. A physical therapist can recommend stretching exercises and massage techniques that can help alleviate pain and inflammation. They can also guide proper footwear and techniques for standing, walking, and engaging in physical activities.
Orthotics
Orthotics, custom-fitted shoe inserts, can support the foot arch and help relieve pressure on the plantar fascia. Orthotics can be especially helpful for individuals with flat feet or high arches.
Night Splints
Night splints are another treatment option for plantar fasciitis in both feet. These splints help stretch the plantar fascia while sleeping, which can help reduce pain and inflammation in the morning.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections can also be used to treat plantar fasciitis in both feet. These injections can reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area. However, they should only be used as a short-term treatment option, as they can have side effects if used over a long period.
Shockwave Therapy
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment option that can help stimulate the healing of the plantar fascia. This therapy uses high-energy sound waves to promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
Surgery
In rare cases where other treatments have not been successful, surgery may be recommended to treat plantar fasciitis in both feet. Surgery typically involves releasing the tension in the plantar fascia or removing a heel spur.
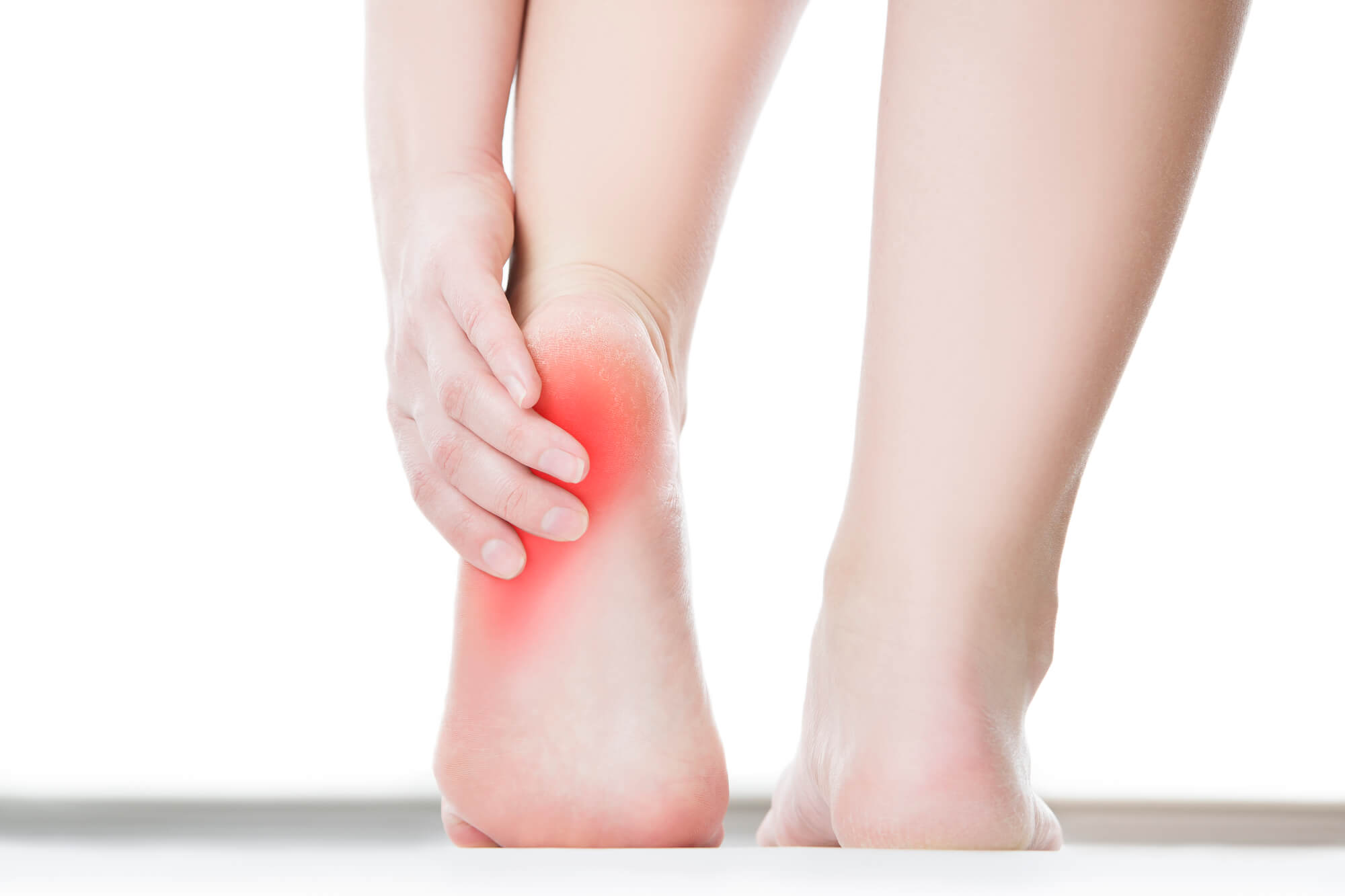
Prevention of Plantar Fasciitis
While plantar fasciitis in both feet can be a painful and debilitating condition, there are several steps you can take to prevent its development or recurrence.
Wear Appropriate Footwear
Appropriate footwear is one of the most important steps to prevent plantar fasciitis in both feet. Shoes should have adequate arch support and cushioning and fit properly to prevent pressure on the plantar fascia. It is also important to replace worn-out shoes regularly.
Stretch Regularly
Stretching regularly can help prevent the development of plantar fasciitis in both feet. Stretching the calf muscles and Achilles tendon can help prevent tightness and tension in the plantar fascia. Stretches such as toe curls and towel stretches can also help prevent plantar fasciitis.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the feet and decrease the risk of developing plantar fasciitis in both feet. Excess weight can increase the load on the plantar fascia, making it more susceptible to injury and inflammation.
Avoid Overuse
Avoiding overuse of the feet can also help prevent the development of plantar fasciitis in both feet. It is important to avoid high-impact activities that place a lot of stress on the feet and to take frequent breaks when standing or walking for long periods.
Use Proper Techniques
Using proper techniques when standing, walking, and engaging in physical activities can also help prevent the development of plantar fasciitis in both feet. Using the correct form and posture is important to avoid placing excess stress on the feet.
Wear Orthotics
Wearing orthotics and custom-fitted shoe inserts can help prevent the development or recurrence of plantar fasciitis in both feet. Orthotics can support the foot arch and help alleviate pressure on the plantar fascia.
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis in both feet can be a painful and debilitating condition, but many treatment options are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. If you are experiencing symptoms of plantar fasciitis, it is important to seek professional help for proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right care and management, many individuals with plantar fasciitis can find relief from pain and inflammation and resume their normal activities.

