Understanding Different Types of Imaging Tests for Foot Conditions
Diagnosing foot and ankle conditions accurately is paramount for effective treatment. Medical imaging is a cornerstone, enabling healthcare providers to visualize internal structures and identify abnormalities. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various imaging techniques used in podiatry, their applications, and how they contribute to patient care.
Key Takeaways
- X-ray imaging is essential for rapidly assessing bone-related issues, such as fractures and deformities, due to its accessibility and ability to visualize bone structures.
- MRI provides superior soft tissue resolution, making it invaluable for diagnosing tendon tears, ligament sprains, and cartilage damage without exposing patients to ionizing radiation.
- CT scans offer high spatial resolution and are ideal for evaluating complex fractures and bone abnormalities, aiding in surgical planning and treatment decision-making.
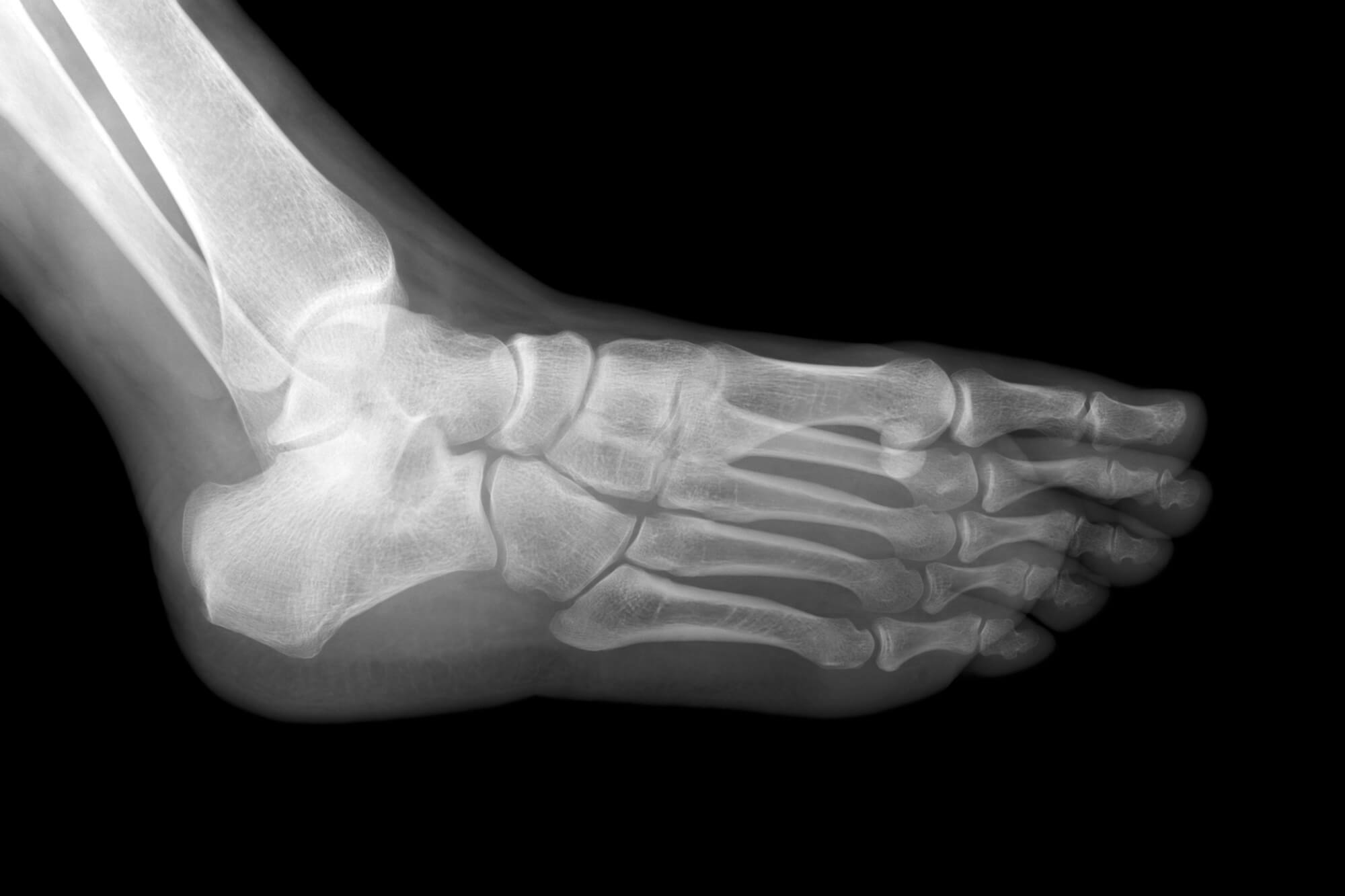
X-Ray Imaging
Overview
X-ray imaging, or radiography, is a foundational tool in orthopedics. It involves exposing the foot and ankle to ionizing radiation to produce images of bones and surrounding tissues.
Application
X-rays capture bone-related issues, including fractures, dislocations, and deformities. They provide detailed images that aid podiatrists in assessing the severity and extent of injuries, guiding treatment decisions.
Advantages of X-Ray Imaging:
- Rapid and Accessible: X-rays are readily available in most medical facilities, allowing for swift diagnosis.
- Bone Visualization: They offer clear visualization of bone structures, making them ideal for detecting fractures and skeletal abnormalities.
X-rays are often the first-line imaging modality due to their accessibility and ability to quickly assess bone injuries. They provide valuable information about the alignment and integrity of bones, helping podiatrists formulate appropriate treatment plans.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Overview
MRI utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues within the foot and ankle.
Application
MRI is indispensable for diagnosing soft tissue injuries like tendon tears, ligament sprains, and cartilage damage. Unlike X-rays, MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast, enabling precise visualization of subtle abnormalities.
Advantages of MRI:
- Soft Tissue Resolution: MRI provides high-resolution images of soft tissues, allowing for accurate diagnosis of tendon and ligament injuries.
- Non-Invasive: It does not involve ionizing radiation, making it safe for patients of all ages.
MRI is particularly valuable in evaluating complex soft tissue injuries that may not be apparent on X-rays or CT scans. It offers multiplanar imaging capabilities, allowing podiatrists to assess the extent of soft tissue damage from various angles.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
Overview
CT scans combine X-ray images to create cross-sectional views of the foot and ankle, offering detailed insights into bone and soft tissue structures.
Application
CT scans excel in diagnosing complex fractures, bone abnormalities, and conditions requiring precise anatomical localization. They provide high-resolution images, aiding in surgical planning and treatment decision-making.
Advantages of CT Scans:
- High Spatial Resolution: CT scans offer detailed views of bone structures, making them ideal for assessing intricate fractures.
- Preoperative Planning: They assist in planning surgical procedures by providing precise anatomical information.
CT scans are often preferred when intricate bone structures such as stress fractures or skeletal deformities need evaluation. They offer superior spatial resolution compared to conventional X-rays, enabling accurate assessment of bone integrity.
Ultrasound Imaging
Overview
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the foot and ankle's internal structures.
Application
Ultrasound is valuable for assessing soft tissue injuries like tendonitis, ligament tears, and bursitis. Its real-time imaging capability allows dynamic evaluation during various foot and ankle movements.
Advantages of Ultrasound:
- Dynamic Assessment: Ultrasound provides real-time visualization of soft tissues, allowing for dynamic evaluation of injuries.
- No Ionizing Radiation: It is safe for pregnant women and children.
Due to its real-time imaging capabilities, ultrasound is particularly useful in guiding interventional procedures, such as injections or aspirations. It offers a dynamic assessment of soft tissue structures, enabling podiatrists to visualize movement abnormalities or fluid collections.
Choosing the Right Imaging Test
Factors to Consider
Several factors influence the choice of imaging test for a foot or ankle condition:
- Nature of Injury: Different imaging modalities are better suited for specific injuries.
- Patient Factors: Considerations such as age, medical history, and pregnancy status may impact the choice of imaging modality.
- Accessibility: The availability of imaging facilities and the urgency of diagnosis play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate test.
The decision-making process involves careful consideration of the clinical presentation, patient preferences, and imaging modality's capabilities. Podiatrists must weigh the benefits and limitations of each imaging test to ensure optimal diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
Conclusion
Accurate diagnosis is fundamental to effective treatment planning and patient outcomes in podiatry. By utilizing advanced imaging technologies such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and ultrasound, podiatrists can obtain detailed insights into foot and ankle conditions, facilitating targeted interventions. At ePodiatrists, we are committed to delivering the highest standard of care through innovative diagnostic approaches. Schedule an appointment with our experienced podiatrists today and embark on the journey to optimal foot and ankle health.

